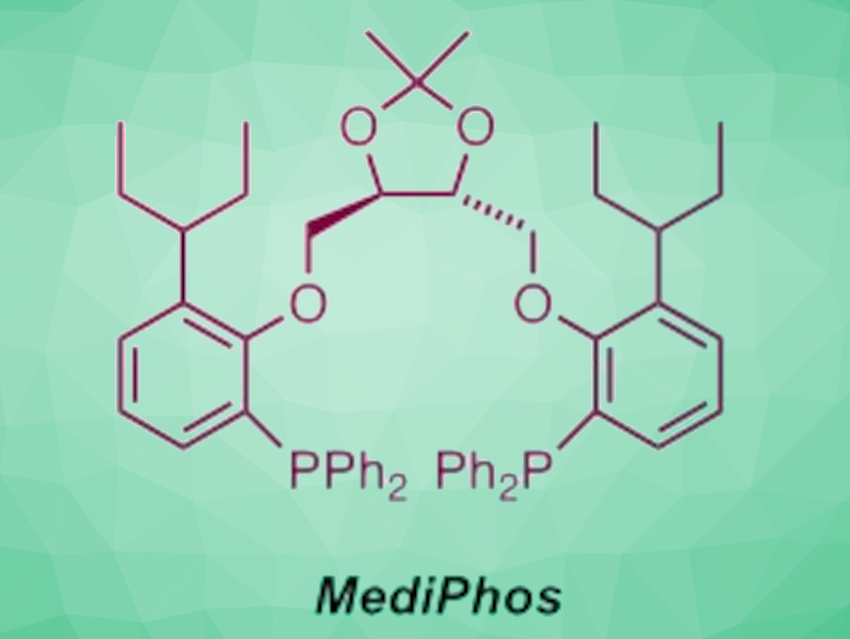
The stereo-controlled N-allylation of amino acid derivatives is useful, e.g., for the synthesis of bioactive peptide-related molecules. There is a reliable and general method for such transformations using Pd-based catalysts with chiral C2-symmetric diphosphane ligands, called MediPhos ligands (example pictured above)
Hans-Günther Schmalz and coworkers from the University of Cologne, Germany, have developed an improved synthesis of MediPhos ligands and demonstrated their usefulness in a particularly challenging transformation. The ligands were prepared in high yields via the reaction of a tartaric acid-derived ditosylate with 2-bromo-5-alkyl-phenols, followed by lithiation and phosphanylation (pictured below). The method allows the preparation of MediPhos ligands with bulkier substituents than previous approaches.
.jpg)
A 3-pentyl substituted MediPhos ligand enabled the researchers to perform the Pd-catalyzed N-allylation of tert-butyl glycinate using a racemic allyl carbonate with high enantioselectivity. The obtained product was then used to synthesize the bicyclic proline-derived dipeptide mimetic ProM-17 in stereochemically pure form. Readily accessible MediPhos ligands could also have other applications in asymmetric transition-metal catalysis.
- Improved Synthesis of MediPhos Ligands and their Use in the Pd‐catalyzed Enantioselective N‐Allylation of Glycine Esters,
Dominik Albat, Martin Reiher, Jörg-Martin Neudörfl, Hans-Günther Schmalz,
Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2021.
https://doi.org/10.1002/ejoc.202100748