Boron impurities such as BCl3 could react with chlorosilanes in industrial processes for the purification of chlorosilanes. Uwe Böhme, Erica Brendler, TU Bergakademie Freiberg, Germany, and colleagues have performed controlled experiments with defined reactants and reaction conditions to investigate the interactions between chlorosilanes and boron compounds in detail. The team reacted different combinations of chlorosilanes such as HSiCl3, H2SiCl2, Si2Cl6, and HSi2Cl5 with boron trichloride in sealed ampoules at up to 80 °C.
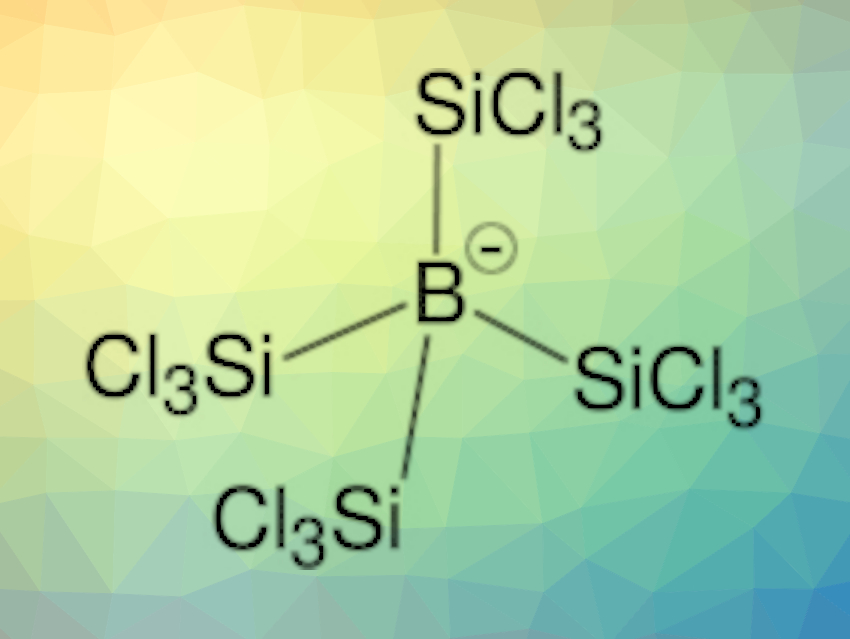
The team observed the formation of a yellow-whitish solid, which was characterized using elemental analysis, mass spectrometry (MS), X-ray crystallography, as well as NMR, infrared (IR), and Raman spectroscopy. The results indicated the formation of H[B(SiCl3)4]. Main group compounds of the type [E(SiCl3)n]− that are stabilized solely by trichlorosilyl groups are known for E = C, Si, Ge, P, and S, but trichlorosilylborates had been mostly unexplored.
The team found that H[B(SiCl3)4] is a superacid and can protonate, e.g., toluene. The corresponding borate ion [B(SiCl3)4]− is a weakly coordinating anion. Often, these types of anions, which can, e.g., stabilize reactive cationic species, contain perfluorinated species. [B(SiCl3)4]− could be useful as a fluorine-free alternative.
- Unexpected Formation of the Highly Symmetric Borate Ion [B(SiCl3)4]−,
Sebastian Bochmann, Uwe Böhme, Erica Brendler, Mike Friebel, Maik Gerwig, Franziska Gründler, Betty Günther, Edwin Kroke, Robert Lehnert, Lars Ruppel,
Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2021.
https://doi.org/10.1002/ejic.202100246