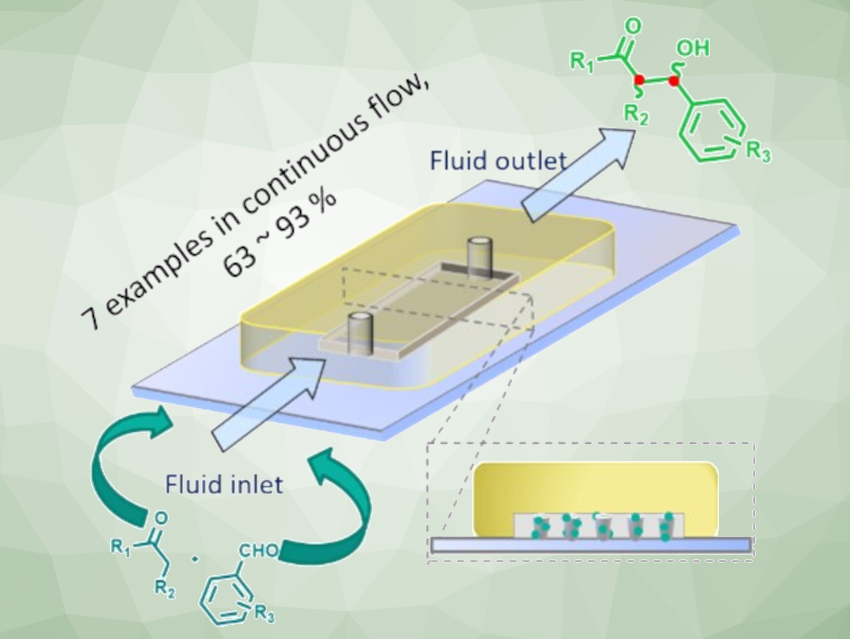
Continuous flow catalysis that uses microfluidic reactors with gel-bound proline organocatalysts is a useful approach in organic synthesis. It has advantages such as the ongoing production of catalyst-free compounds and easy product isolation by evaporation. It also allows the online monitoring of the reaction and offers the possibility to adjust the reaction parameters while the reaction is running. In addition, gel-bound catalysts, which are integrated within a crosslinked, swollen polymer network, increase the share of accessible catalyst—from only the surface area to the bulk volume.
Dirk Kuckling, Paderborn University, Germany, and colleagues have developed a continuous-flow method for the asymmetric synthesis of differently substituted aldol products. The team used a bifunctional prolineamide catalyst, which was immobilized using a photopolymerization with methyl methacrylate (MMA) as the gel-building component and ethylene glycol dimethacrylate (EGDMA) as the crosslinker. The team placed 662 catalytically active polymer dots in a microfluidic reactor with a volume of 100 µl. This reactor was then used for organocatalyzed asymmetric aldol reactions of various aromatic aldehydes with different ketones.
The desired products were obtained within minutes, under mild conditions, and in good to almost quantitative yields. The developed reactor setup showed long-term stability, with high conversion and good selectivity over up to 144 hours using the model substrates cyclohexanone and 4-nitrobenzaldehyde. According to the researchers, this work could be extended to other organocatalyzed reactions under continuous flow.
- Direct asymmetric aldol reaction in continuous flow using gel-bound organocatalysts,
Carsten J. Schmiegel, Rene Baier, Dirk Kuckling,
Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2021.
https://doi.org/10.1002/ejoc.202100268