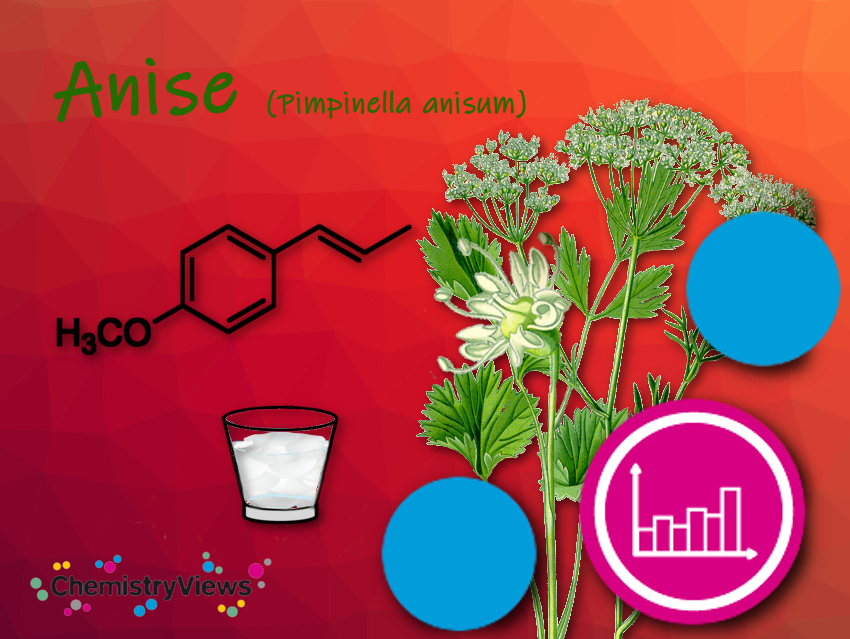
Anise seed is used as a spice either ground or whole. Ground anise should be consumed soon, as it loses its seasoning power relatively quickly. Anise is used as a baking spice for aniseed cookies, rusks, pretzels and bread, and to season dishes such as sauces, vegetables, fish dishes, salads, or plum jam.
Anise seeds are considered a digestive (can reduce intestinal gas and flatulence), an antispasmodic (can prevent muscle spasms), and an expectorant (helps against coughs). They also have antibacterial properties and much more.
Aniseed-scented spirits and liqueurs can be found all over the world, such as the Italian Sambuca, Greek Ouzo, Bulgarian and Macedonian Mastika, French Absinthe, Anisette and Pastis, Spanish Anís del Mono, Anísado and Herbs de Mallorca, Turkish and Armenian Rakı, Lebanese, Egyptian, Syrian, Jordanian and Israeli Arak, Algerian Anisette Cristal, Colombian Aguardiente, and Mexican Xtabentún.


Anise (Pimpinella anisum) and star anise (Illicium verum) are not related, although both contain anethole, which produces the characteristic anise flavor, and are used to produce anise extract. Anise is the source of the extract and seeds used in European, Mediterranean, and Middle Eastern cuisine. Star anise is native to China. Because star anise is cheaper to produce, today much of the anise essential oil is extracted from star anise rather than anise.
References
- Ruth Genuneit, Gewürze und Backtriebmittel in der Weihnachtsbäckerei, Institut Dr. Flad, Stuttgart, Germany, 2019. (Retrieved November 24, 2020)
- William Cook, The Physiomedical Dispensatory, 1869. (Retrieved November 24, 2020)
Also of Interest
- Chemistry Advent Calendar 2020
ChemistryViews 2020.
Daily highlights from the chemistry of spices