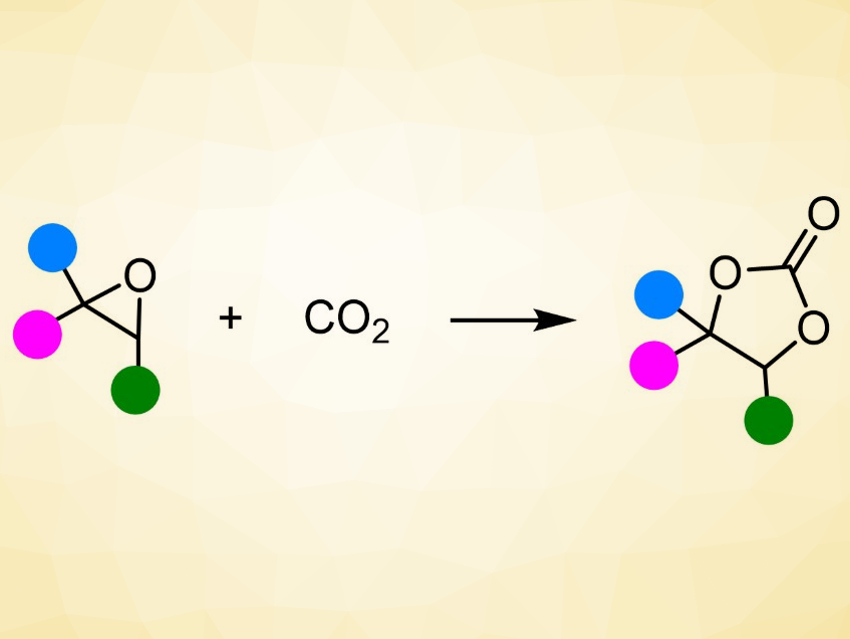
The greenhouse gas CO2 can be used as an inexpensive, abundant, and renewable chemical feedstock. The reaction of CO2 with epoxides (pictured) is particularly interesting in this context. It is an atom-economic reaction and an excellent example of green, sustainable chemistry. The obtained products, cyclic carbonates, have applications, e.g., as intermediates in organic synthesis, green solvents, electrolytes in lithium-ion batteries, polymer building blocks, and additives in cosmetics.
Thomas Werner, Leibniz Institute for Catalysis, Rostock, Germany, and colleagues have used phenol-functionalized phosphonium salts as an organocatalysts for the reaction of CO2 with epoxides to give cyclic carbonates. The team used (2-hydroxyphenyl)diphenyl(propyl)phosphonium iodide as the catalyst for the solvent-free reaction of different substituted epoxides with CO2 at room temperature to 80 °C.
Using this approach, various cyclic carbonates were prepared in excellent yields. Both terminal and more challenging internal epoxides were converted. The reaction has a good functional group tolerance and can be performed on a multi‐gram scale.
- Catalytic, kinetic and mechanistic insights into the fixation of CO2 with epoxides catalyzed by phenol functionalized phosphonium salts,
Yuya Hu, Zhihong Wei, Anna Frey, Christoph Kubis, Chang-Yue Ren, Anke Spannenberg, Haijun Jiao, Thomas Werner,
ChemSusChem 2020.
https://doi.org/10.1002/cssc.202002267



![Synthesis of [c2]Daisy Chains via Mechanochemistry](https://www.chemistryviews.org/wp-content/uploads/2025/04/202504_RotaxanesWithSolidStateMechanochemistry-125x94.png)