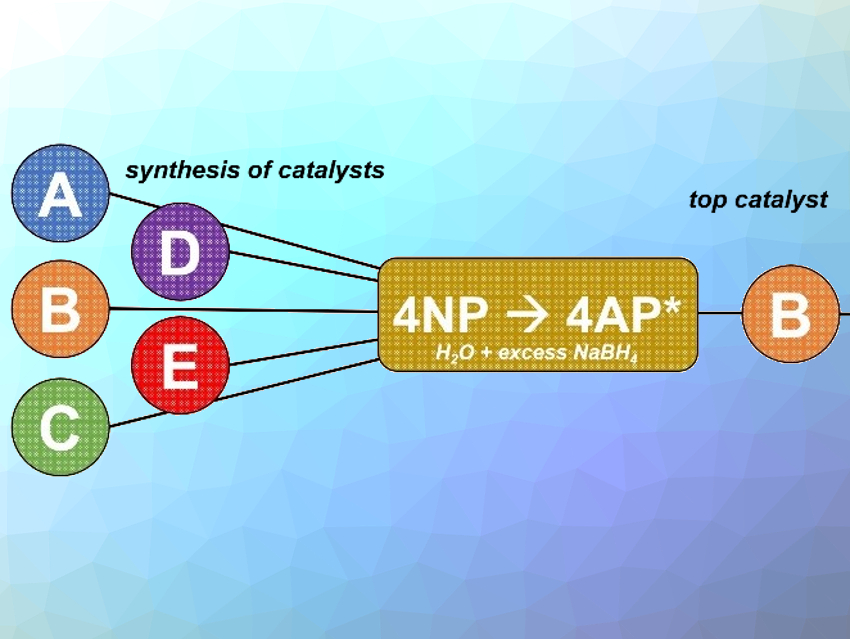
The catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol (4NP) to 4-aminophenol (4AP) with excess NaBH4 is a model reaction for quantifying the catalytic activity of nanoparticles. The near-universal use of this benchmark provides a unifying point of comparison when designing new heterogeneous catalysts. Another common use of the model is for the selection of the best catalysts from a larger candidate pool (pictured), where the most active catalyst for 4NP reduction is selected and then tested on an expanded substrate scope.
Titel Jurca, University of Central Florida, Orlando, USA, and colleagues observed that the ability of this universal probe to predict the most active catalyst from a candidate pool was often inconsistent, leading to false positives and negatives. Broader screening revealed that the most active catalyst for 4NP reduction was not always the most active catalyst for an expanded substrate scope.
To maintain the efficient nature of the 4NP probe but improve the outcome, the team has developed a multi-nitrophenol cocktail screening protocol. Instead of just 4NP, the team used a mixture of 4NP, 4‐amino-3‐nitrophenol (4A3NP), 2‐amino-5‐nitrophenol (2A5NP), and 4‐amino-2‐nitrophenol (4A2NP), which were all used together in a single run to screen catalyst candidates. The reduction of the nitrophenols cocktail proceeds with no deleterious side reactions. The cocktail-based screening gives better predictions of the broader average performance of catalysts than traditional 4NP-only screening.
The findings suggest that a cocktail approach can lead to better outcomes. The next step would be the development of optimized “cocktail recipes”.
- Using a Nitrophenol Cocktail Screen to Improve Catalyst Down-selection,
Lorianne R. Shultz, Lin Hu, Xiaofeng Feng, Titel Jurca,
ChemPhysChem 2020.
https://doi.org/10.1002/cphc.202000400