The functionalization of molecular metal oxides, so-called polyoxometalates (POMs), with organic groups can open up new synthetic possibilities. For example, it could allow the assembly of POMs into nanostructured supramolecular architectures for the bottom‐up design of molecular functional materials. However, the number of organofunctionalization routes for POMs is limited.
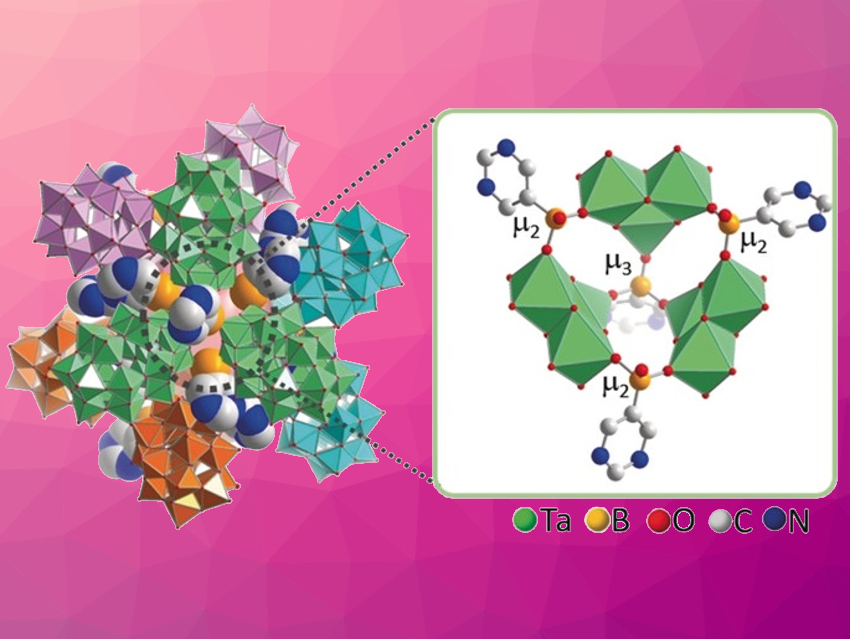
Zhiping Zheng, Southern University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen, China, Carsten Streb, Ulm University, Germany, Xuenian Chen, Henan Normal University, Xinxiang, China, and Zhengzhou University, China, and colleagues have developed a new way to functionalize Dawson-type POM anions with the formula [M3P2W15O62]9– (M = Nb, Ta) with aromatic boronic acids. The functionalized POMs‐based were synthesized via reactions of [(MO2)3P2W15O62]9– (M = Nb, Ta) with either 3‐pyridineboronic acid or 5‐pyrimidinylboronic acid in an acidic aqueous solution at 75 °C.
The boronic acids bind specifically at the Nb and Ta sites of the POMs, which leads to self-recognition and regiospecific aggregation. They form bridging linkages between the Dawson anions (pictured above on the right), so that nanostructured capsules are obtained. Two classes of capsules were identified by single-crystal X-ray diffraction: one type contained four Dawson anions (ca. 3 nm in diameter), while the other type contained twelve Dawson anions (ca. 4 nm in diameter, pictured). Such nanocapsules could have applications in confinement-controlled catalysis and size-selective guest transport.
- Organoboron-Functionalization Enables the Hierarchical Assembly of Giant Polyoxometalate Nanocapsules,
Shujun Li, Yanfang Zhou, Nana Ma, Jie Zhang, Zhiping Zheng, Carsten Streb, Xuenian Chen,
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020.
https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202003550