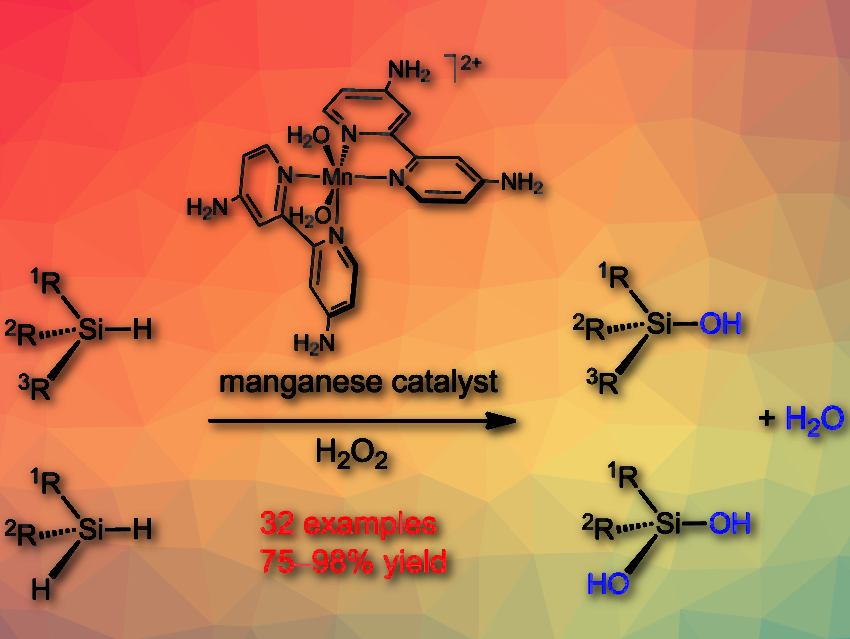
Silanols have broad applications in organic synthesis and material chemistry. However, the selective synthesis of silanols and silandiols is still challenging.
Chaoqun Li, Jianliang Xiao, Shaanxi Normal University, China, and colleagues have developed a well-defined molecular manganese catalyst that allows for highly selective oxidation of various hydrosilanes and dihydrosilanes with H2O2 as an oxidant. The oxidation is readily performed using 1–2 mol % of the manganese catalyst in acetone at room temperature, requiring neither an acid or base additive nor inert gas protection while affording silanols and silandiols in high yields.
The simple manganese salt, Mn(ClO4)⋅6 H2O had no catalytic activity. The researchers found that ligands play a key role in enabling this manganese catalysis. They used a range of 4,4′‐disubstituted bipyridines and observed that the electron‐rich 4,4′‐diamino bipyridine combined with Mn(ClO4)2 shows the best catalytic activity. Mechanistic studies suggest that the oxidation proceeds via a concerted reaction of a MnIII-OOH species with the hydrosilane.
Featuring fast, clean oxidation under mild conditions with no noxious by-products generated, the protocol provides an ecologically benign approach to both silanols and silandiols.
- Selective Manganese-Catalyzed Oxidation of Hydrosilanes to Silanols under Neutral Reaction Conditions,
Kaikai Wang, Jimei Zhou, Yuting Jiang, Miaomiao Zhang, Chao Wang, Dong Xue, Weijun Tang, Huamin Sun, Jianliang Xiao, Chaoqun Li,
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019.
https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201900342