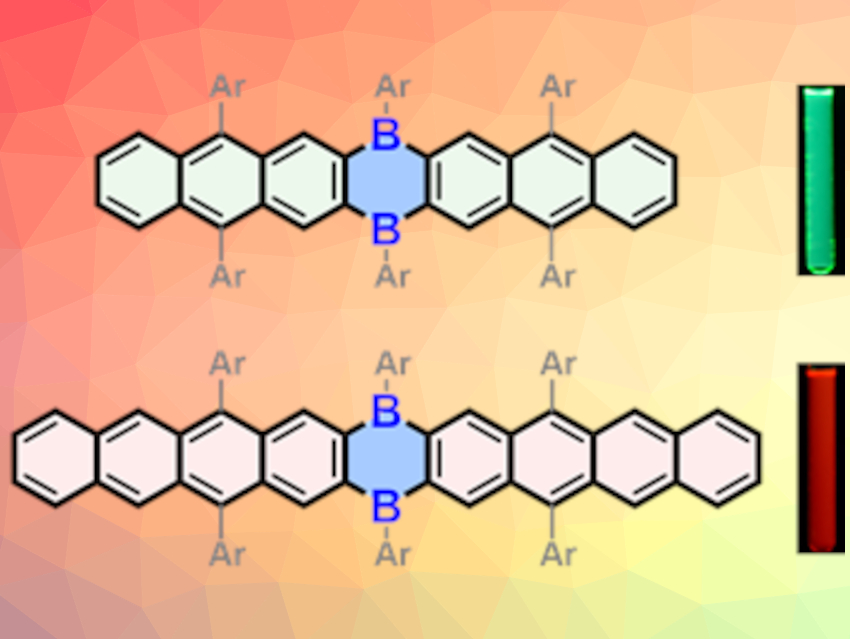
Acenes are polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons made up of linearly fused benzene rings. Heteroacenes incorporate heteroatoms in their skeletons and are promising structures for organic functional materials. Boron-embedded boraacenes, for example, possess unique optoelectronic properties. However, long boraacenes (n ≥ 6) are challenging to synthesize and isolate.
Xiao-Ye Wang, Nankai University, Tianjin, China, and colleagues have pushed the length limits of boraacenes by synthesizing the longest boron-embedded heteroacenes to date—dihydrodiboraheptacene and dihydrodiboranonacene (pictured). The key step for the synthesis of both compounds is an Si/B exchange of trimethylsilyl groups with boron tribromide to construct the linear backbone from two fragments, followed by substitution with bulky aryl groups.
The boron-embedded heptacene is highly stable, whereas the boron-embedded nonacene is air-sensitive. Both compounds exhibit unique anti-Kasha luminescence (a direct emission from high excited states) and high photoluminescence quantum yields (boron-embedded heptacene: ca. 98 %; boron-embedded nonacene: 51 %). This work could potentially create new opportunities for the development of boraacene-based functional materials with useful optical properties.
- Pushing the Length Limit of Dihydrodiboraacenes: Synthesis and Characterizations of Boron‐Embedded Heptacene and Nonacene,
Cheng Chen, Ming‐Wei Wang, Xing‐Yu Zhao, Shuang Yang, Xing‐Yu Chen, Xiao‐Ye Wang,
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022.
https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202200779