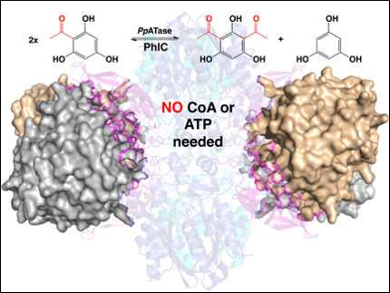
One of the most well-known reactions for synthesizing aromatic ketones, the Friedel-Crafts acylation, is also possible in an environmentally friendly, biocatalytic manner. Wolfgang Kroutil, Karl Gruber, Austrian Centre of Industrial Biotechnology (ACIB), University of Graz, and BioTechMed-Graz, Austria, and colleagues have identified an enzyme that is produced by Pseudomonas protegens and catalyzes the Friedel–Crafts C‐acylation of phenolic substrates in aqueous solution.
The team determined the 3D structure of this bacterial multicomponent acyltransferase (PpATase) using X-ray crystallography and identified the residues which are important for catalysis using site-directed mutagenesis. The multimeric enzyme consists of three subunits called PhlA, PhlB, and PhlC. Only residues from the PhlC subunits seem to be involved in the acyl transfer reaction.
The use of the discovered enzyme eliminates the costly disposal of unwanted by-products usually obtained by chemical Friedel-Crafts acylations, as well as the need for a catalyst such as AlCl3. It also allows the production of the desired substances with higher purity, which is important in the pharmaceutical and cosmetics industry, as well as for flavor production. The researchers are currently working on enabling the transfer of larger chemical groups than acetyl. To this end, variants of the enzyme are being developed.
- Structure and Catalytic Mechanism of a Bacterial Friedel-Crafts Acylase,
Tea Pavkov-Keller, Nina G. Schmidt, Anna Żądło‐Dobrowolska, Wolfgang Kroutil, Karl Gruber,
ChemBioChem 2018.
https://doi.org/10.1002/cbic.201800462