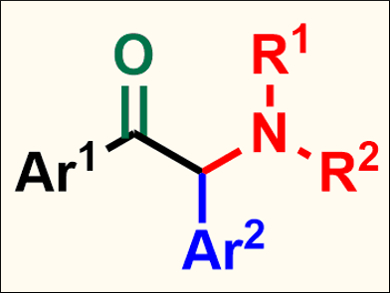
Multi-component cascade reactions are a useful strategy for the fast synthesis of complex molecules. Transition-metal-catalyzed three-component cascade reactions are often used. In contrast, more complicated four-component intermolecular cascade processes still remain challenging. This is due to the difficulty in controlling the reactivity of the components and the selectivity of the reactions.
Jianbo Wang, Peking University, Beijing, China, Zhenhua Zhang, China Agricultural University, Beijing, China, and colleagues have developed a Pd(0)-catalyzed intermolecular four-component cascade reaction of aryl halides, CO, N-tosylhydrazones, and amines, which gives α-amino ketones (pictured) in good yields. The team used Pd2(dba)3 as a catalyst (dba = dibenzylideneacetone), 1,3‐bis(diphenylphosphino)propane (DBBP) as a ligand, K2CO3 as a base, and 1,4‐dioxane as the solvent.
Control experiments and density functional theory (DFT) calculations provided insight into the detailed sequence of the reaction. The team proposes a mechanism that involves the generation of an acylpalladium species by carbonylation, followed by a Pd(II) carbene formation and a migratory insertion to give an alkylpalladium(II) species, which is trapped by the amine to give the final product.
- Pd(0)-Catalyzed Four-Component Reaction of Aryl Halide, CO, N-Tosylhydrazone, and Amine,
Jianbo Wang, Yiyang Liu, Zhen Zhang, Songnan Zhang, Yan Zhang, Zhenhua Zhang,
Chem. Asian J. 2018.
https://doi.org/10.1002/asia.201801324