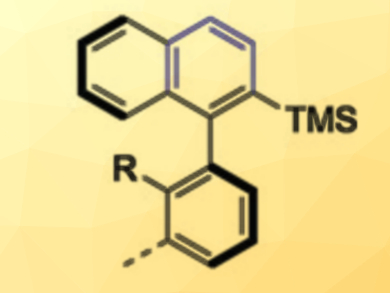
There is a range of synthetic methods that control the configuration of stereogenic centers. In contrast, control over other chirality elements such as stereogenic axes is often limited. Usually, a multistep sequence that relies on the proximity of the stereogenic units in the chiral reagent and in the product is required for the selective conversion of stereocenter-containing substrates into axially chiral products.
Achim Link and Christof Sparr have used readily available chiral 1,5-bifunctional organomagnesium alkoxide reagents to convert simple aryl esters into enantioenriched axially chiral biaryl silanes (example pictured). In a diastereoselective double addition, the stereochemical information encoded in the reagent is first transferred to a transient stereocenter close to a rotationally restricted bond. During an in-situ reduction, the planarization of both stereocenters then proceeds with a high level of control in a central-to-axial chirality conversion.
Using this mild one-step transformation, various biaryl silanes are accessible in a highly enantioenriched form. Research fields such as catalysis, medicinal chemistry, or materials science could profit from the direct transformation of esters into axially chiral compounds.
- Remote Central-to-Axial Chirality Conversion: Direct Atroposelective Ester to Biaryl Transformation,
Achim Link, Christof Sparr,
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018.
https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201803472