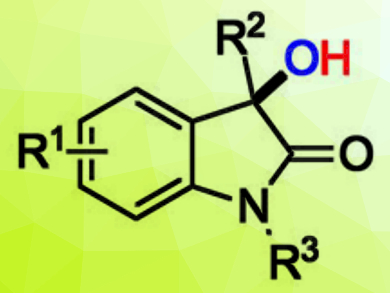
3-Hydroxy-2-oxindoles (example pictured) are useful biologically active molecules, and there is a need for efficient methods for their synthesis under mild conditions.
Wen-Ting Wei, Ningbo University, China, have developed a base- and metal-free C(sp3)–H hydroxylation of 2-oxindoles. The reaction is promoted by TEMPO (2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine N-oxide) and uses atmospheric air as a hydroxylation reagent in THF (tetrahydrofuran) at room temperature.
The proposed reaction mechanism involves TEMPO reacting with the enol form of the 2-oxindole, followed by a reaction with O2 that generates a superoxide anion. This anion regenerates TEMPO and is converted to a peroxide. In a final step, the peroxide is cleaved to give the desired product.
This protocol provides a mild and simple strategy for the construction of C–O bonds in moderate to good yields. The reaction can convert a wide range of substituted 2-oxindoles with a variety of functional groups.
- TEMPO-Promoted C(sp3)−H Hydroxylation of 2-Oxindoles at Room Temperature,
Wen-Ming Zhu, Wen-Hui Bao, Wei-Wei Ying, Wei-Ting Chen, Yi-Ling Huang, Guo-Ping Ge, Gan-Ping Chen, Wen-Ting Wei,
Asian J. Org. Chem. 2018.
https://doi.org/10.1002/ajoc.201700660