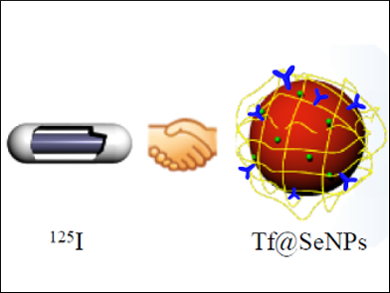
Cancer radiotherapy with 125I seeds has shown long-term higher efficacy and lower side effects than traditional X-ray radiotherapy owing to low dosage and continuous radiation. However, it is still limited by radioresistance in clinical applications. Therefore, the design and synthesis of sensitizers that could enhance the sensitivity of cancer cells to 125I seeds is of great importance.
Selenium nanoparticles (SeNPs) are of interest due to their high potential for cancer chemotherapy and as carriers of anticancer drugs. Tianfeng Chen, Jinan University, China, and colleagues have designed and synthesized cancer-targeted SeNPs and found that they have synergetic effects in combination with 125I seeds. The combination inhibits cancer-cell growth and colony formation through the induction of cell apoptosis and cell-cycle arrest. The combined treatment effectively activates intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) overproduction and prevents the self-repair of cancer cells.
The combination of SeNPs with 125I seeds could be useful as a safe and effective strategy for next-generation cancer chemo-radiotherapy in clinical applications.
- Cancer-targeted Selenium Nanoparticles Sensitize Cancer Cells to Continuous γ Radiation to Achieve Synergetic Chemo-Radiotherapy,
Leung Chan, Lizhen He, Binwei Zhou, Shouhai Guan, Mingjun Bo, Yahui Yang, Ying Liu, Xiao Liu, Yanyang Zhang, Qiang Xie, Tianfeng Chen,
Chem. Asian J. 2017.
DOI: 10.1002/asia.201701227