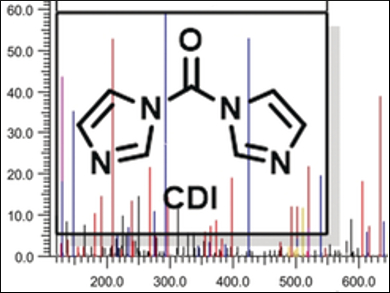
The collision-induced dissociation mass spectrometry of proteins produces characteristic ions, which can hint at the 3D structure of the parent material. In this approach, cleavable chemical cross-linkers are useful for obtaining detailed structural information across short protein distances.
Andrea Sinz and colleagues, Martin Luther University Halle-Wittenberg, Halle, Germany, have developed a 1,1’-carbonyldiimidazole cross-linking reagent (CDI, pictured) that bridges primary amines and hydroxyl groups in proteins with a short spacer length of only one carbonyl unit (ca. 2.6 Å). Urea and carbamate cross-linked products were formed efficiently under aqueous physiological conditions between pH 7.8 and 8.0 and at temperatures above 10 °C.
CDI does not generate the most common sources of cross-link misassignment, i.e., carboxylic acids produced by irreversible hydrolysis. The analytical technique was successfully applied to cross-linked adducts of bovine serum albumin (BSA), the tumor suppressor p53, and the guanylyl cyclase-activating protein-2 (GCAP-2). CDI delivers structural data on globular as well as intrinsically disordered proteins. It could be useful in the arsenal of cross-linkers available for protein structure elucidation by mass spectrometry. According to the researchers, it is an easy-to-use and commercially available, low-cost reagent.
- The First “Zero-Length” Mass Spectrometry-Cleavable Cross-Linker for Protein Structure Analysis,
Christoph Hage, Claudio Iacobucci, Anne Rehkamp, Christian Arlt, Andrea Sinz,
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017.
DOI: 10.1002/anie.201708273