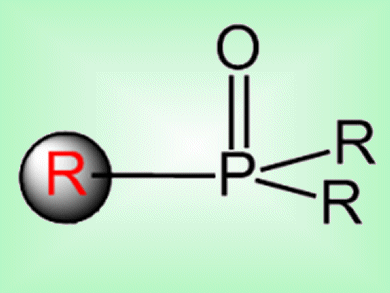
C—P bond construction is important in the synthesis of modified nucleosides, nucleotides, and other phosphine-containing ligands for use in catalysis or, as in the case of nucleoside analogues, to treat viral infections and cancer. Most cross-coupling routes to C—P bonds can only use aryl iodides as coupling partners.
Yong-Min Liang and co-workers, Lanzhou University, China, have reported a way to make C—P bonds via a copper-catalyzed decarboxylative coupling with R2P(O)H. This allowed alkenyl acids, alkynyl acids, and N-benzylproline to be used as coupling partners. This method also exhibits the best regio- and chemoselectivity reported so far for C—P coupling. It demonstrated good functional-group tolerance and good scale-up possibilities.
- Copper-Catalyzed C–P Coupling through Decarboxylation
J. Hu, N. Zhao, B. Yang, G. Wang, L.-N. Guo, Y.-M. Liang, S.-D. Yang,
Chem. Eur. J. 2011.
DOI: 10.1002/chem.201003561