1,3-Oxazines are a well-known structural motif for biologically active substances. They exhibit antifungal, antibiotic, antiviral, and antitumor properties and are also used as acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibitors; potential targets for Alzheimer’s drugs.
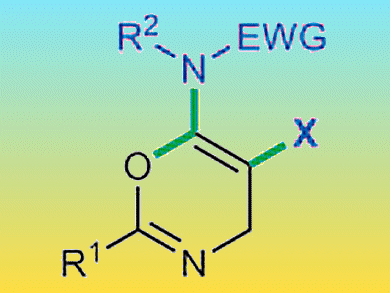
Stephen Hashmi and co-workers, Ruprecht-Karls-Universität Heidelberg, Germany, have reported the synthesis of a new class of oxazine derivatives. The synthesis used propargylcarboxamide, a protected amine, and a source of chloride along with a copper catalyst to form a range of 5-halo-4H-1,3-oxazine-6-amines. This assembly of three simple components into an oxazine was tolerant of a wide range of functional groups. It was demonstrated that the products could be further functionalized by palladium cross-coupling reactions. This provides a simple route to new aminooxazine derivatives of pharmaceutical interest.

Images: (c) Wiley-VCH
- Synthesis of 5-Halo-4H-1,3-oxazine-6-amines by a Copper-Mediated Domino Reaction
A. S. K. Hashmi, A. M. Schuster, M. Zimmer, F. Rominger,
Chem. Eur. J. 2011.
DOI: 10.1002/chem.201100423