Quinazolines (pictured) are an important class of chemical compounds, found in many biologically active molecules and natural products. To date, most synthetic methods for these compounds use stoichiometric amounts of oxidant and noble-metal catalysts.
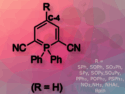
Li-Zhu Wu and colleagues, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, have developed an efficient one-pot strategy for the aerobic tandem oxidative synthesis of 2-substituted quinazolines under visible-light irradiation. The team used the cheap and commercially available dye Eosin Y as an organic photosensitizer and molecular oxygen as the terminal oxidant. The reaction proceeds via condensation of 2-aminobenzylamines and aldehydes, followed by an aerobic dehydrogenative reaction under green light.
The researchers converted a variety of substituted aldehydes and 2-aminobenzylamines to their corresponding quinazolines in good to excellent yields. Electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) spectroscopy shows that a superoxide radical anion (O2•–) is the active species for this transformation.
- Superoxide Radical Anion-Mediated Aerobic Oxidative Synthesis of 2-Substituted Quinazolines under Visible Light,
Xiu-Long Yang, Qing-Yuan Meng, Xue-Wang Gao, Tao Lei, Cheng-Juan Wu, Bin Chen, Chen-Ho Tung, Li-Zhu Wu,
Asian J. Org. Chem. 2017.
DOI: 10.1002/ajoc.201600550