There have been attempts to develop catalytic arylation reactions using phenol and its simple derivatives instead of aryl halides. This would lead to more economical and “greener” chemical processes. The vast majority of efforts focused on developing cross-coupling reactions of inert phenol derivatives including aryl ethers, esters, and carbamates. These have involved the use of low-valent nickel catalysts. However, applications of such reactions to cross-coupling with C–H bonds have had only limited success.
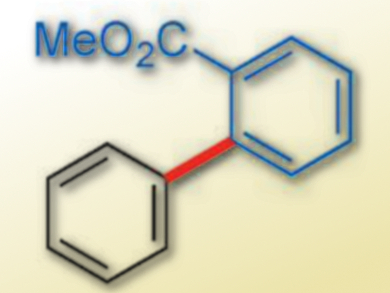
Mamoru Tobisu, Naoto Chatani, Osaka University, Japan, and colleagues have established a protocol that permits aryl carbamates to be coupled to arene C–H bonds using a rhodium-based catalyst. The group developed a rhodium catalyst bearing two N-heterocyclic carbene (NHC) ligands, which can activate both an inert C(aryl)–O bond of an aryl carbamate and a C–H bond of an arene and catalyze cross-coupling reactions. The catalyst is generated in situ from [RhCl(C2H4)2]2 and a substituted NHC ligand. The reaction gives a range of biaryls (example pictured) in good to excellent yields.
- C–O Activation by a Rhodium Bis(N-Heterocyclic Carbene) Catalyst: Aryl Carbamates as Arylating Reagents in Directed C–H Arylation,
Mamoru Tobisu, Kosuke Yasui, Yoshinori Aihara, Naoto Chatani,
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017.
DOI: 10.1002/anie.201610409