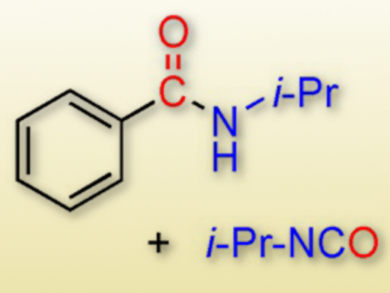
Palladium-catalyzed aminocarbonylation reactions between aryl halides and amines generally require toxic CO gas as the carbonyl source. Carbon monoxide-free palladium-catalyzed aminocarbonylation reactions using various CO surrogates have become an attractive research goal.
Chul-Ho Jun, Yonsei University, Korea, and colleagues developed a method for the synthesis of amides and phthalimides from aryl halides. They used carbodiimides and formic acid as the carbonyl source, and palladium(II) acetate together with an imidazole ligand as the catalyst.
This process is the first example of an in situ formation of CO from formic acid and a carbodiimide in the presence of Pd(OAc)2. The reaction provided the aminocarbonylation products (amides and phthalimides) of aryl halides along with their isocyanate co-products in a simple and efficient manner.
- Synthesis of Amides and Phthalimides via a Palladium Catalyzed Aminocarbonylation of Aryl Halides with Formic Acid and Carbodiimides,
Yong-Sik Seo, Dong-Su Kim, Chul-Ho Jun,
Chem. Asian J. 2016, 11, 3508–3512.
DOI: 10.1002/asia.201601421