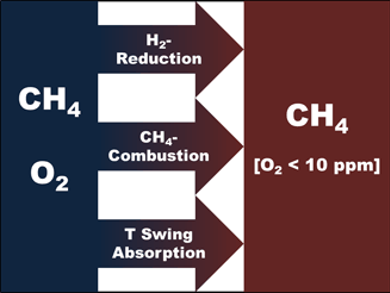
Besides methane and carbon dioxide as the main components, biogas also contains traces of other gases, particularly oxygen. The injection of biomethane into the natural gas grid, which opens additional storage, transport, and usage options, does not only require the removal of the CO2, sulfur components, and water, but also the lowering of oxygen levels.
Sebastian Wohlrab and his team at the Leibniz Institute for Catalysis at the University of Rostock, Germany, tested and characterized three conventional methods for trace oxygen removal from a simulated biogas: (i) catalytic reduction of oxygen with hydrogen; (ii) absorption on oxygen storage materials; (iii) catalytic conversion of oxygen with methane as reductant.
All three methods resulted in oxygen removal below a residual level of 10 ppmv. Therefore, they are, in principal, applicable in biogas plants with an integrated biomethane isolation unit, which is necessary for the injection into the natural gas grid. However, hydrogen admixing, temperature swing cycles, and side product isolation should be objectively considered. The practical handling of these issues will determine the technology transfer from the lab to the plant.
- Methods for the Trace Oxygen Removal from Methane-Rich Gas Streams,
T. Peppel, D. Seeburg, G. Fulda, M. Kraus, U. Trommler, U. Roland, S. Wohlrab,
Chem. Eng. Technol. 2017, 40, 153–161.
DOI: 10.1002/ceat.201600171