High-pressure dispersion and emulsification in microchannels have several advantages such as the possibility to use small educt batches, narrow residence time distributions, and a relatively accurate adjustment of the stresses induced with a good reproducibility. These advantages lead to a wide range of applications, especially for pharmaceutical products with their high requirements in hygiene, product fineness, and polydispersity.
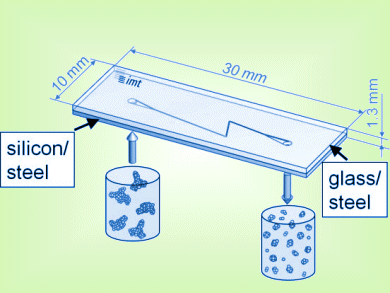
A team led by S. Büttgenbach, C. Müller-Goymann and A. Kwade, TU Braunschweig, Germany, have investigated the influence of the microchannel geometry on the production of nanosuspensions and nanoemulsions by using tailor-made microchannel geometries.
They show that straight channels and Z-channels appear to be least efficient, while orifice channels and T-channels provide the highest efficiencies. Beside the channel geometry, the channel height has a crucial effect on dispersion as well as on emulsification efficiency.
- Effect of Microchannel Geometry on High-Pressure Dispersion and Emulsification
T. Gothsch, J. H. Finke, S. Beinert, C. Lesche, J. Schur, S. Büttgenbach, C. Müller-Goymann, A. Kwade,
Chem. Eng. Technol. 2011, 34 (3), 335.
DOI: 10.1002/ceat.201000421