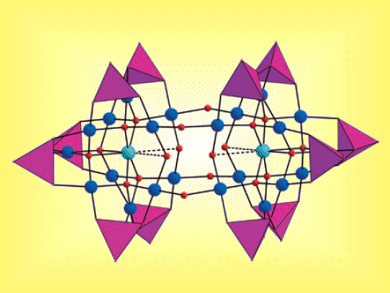
Working with colleagues from Jacobs University in Germany, Massey University in New Zealand, Florida State University in the USA, and the Université Paris-Sud Bâtiment in France researchers have prepared and fully characterized the largest noble metalate reported to date (see structure, Cu turquoise, Pd blue, O red balls, {PO4} purple tetrahedra).
The compound was isolated as a hydrated sodium salt and represents a novel, discrete, solution-stable, double-cuboid-shaped copper(II)-containing polyoxo-22-palladate(II). This polyanion contains the largest number of palladium ions yet found in polyoxopalladate chemistry and the bonding of each Cu(II) ion involves the rare eightfold oxo-coordination. The physical property of this new species was also studied through IR, UV/Vis, and EPR spectroscopy, thermogravimetric analysis, electrochemistry, and magnetic susceptibility measurements. The magnetic exchange interaction between the two Cu(II) ions is unexpectedly large, thus having possible implications for future theoretical investigations of magnetic interactions in such species.
- Synthesis and Characterization of the Dicopper(II)-Containing 22-Palladate(II) [CuII2PdII22PV12O60(OH)8]20–
M. Barsukova-Stuckart, N. V. Izarova, G. B. Jameson, V. Ramachandran, Z. Wang et al.,
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011.
DOI: 10.1002/anie.201006734 - M. Barsukova-Stuckart, N. V. Izarova, G. B. Jameson, V. Ramachandran, Z. Wang et al.,
Angew. Chem. 2011.
DOI: 10.1002/ange.201006734