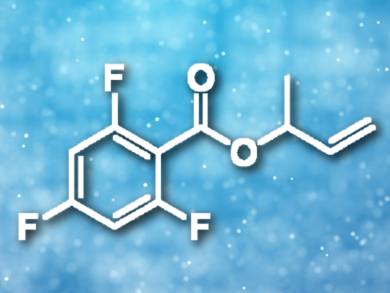
The addition of a carboxylic acid to a diene is a key step in converting the abundant commodity chemical butadiene into reactive allylic esters. Modification of a chloro(1,5-cycloctadiene)rhodium(I) dimer with tris(2-furyl)phosphine provides a catalyst for the addition of fluorinated benzoic acids to dienes, including butadiene.
Jon A. Tunge, University of Kansas, Lawrence, USA, and colleagues have developed a rhodium-catalyzed addition of fluorinated carboxylic acids to butadiene that proceeds via rhodium allyl intermediates. Best results were obtained using 2.5 mol% of the rhodium catalyst with 5 mol% tri(2-furyl)phosphine as a ligand in toluene at 80 °C with a reaction time of 24 h. The resulting branched allylic esters (example pictured) are excellent substrates for further catalytic functionalization.
Mechanistic experiments indicate that the catalytic process is reversible, thus the yield of the ester product is dependent on the acidity of the carboxylic acid reactant. Importantly, the results provide guidelines for choosing acids that will give high yields of addition or, alternatively, acids that are compatible and non-reactive with dienes.
- Catalytic Addition of Fluorinated Benzoic Acids to Butadiene,
Tapan Maji, Mary L. Maliszewski, Mary K. Smith, Jon A. Tunge,
ChemCatChem 2016, 8, 3343–3346.
DOI: 10.1002/cctc.201600654