The direct functionalization of benzylic C(sp3)–H bonds is a straightforward approach to the synthesis of aromatic compounds that are useful, e.g., in medicinal chemistry and materials science. There are deprotonative benzylic transformations using relatively mild hexamethyldisilazide (HMDS) bases. However, toluene derivatives are not very reactive due to their comparatively low acidity. Thus, these reactions often require an excess amount of toluene substrates.
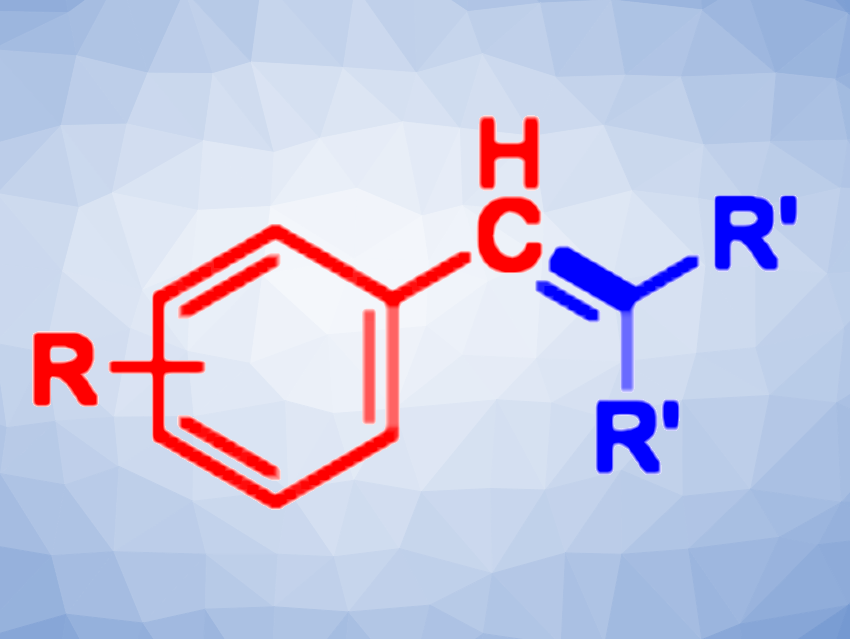
Masanori Shigeno, Tohoku University, Sendai, Japan, JST, PRESTO, Kawaguchi, Saitama, Japan, Yoshinori Kondo, Tohoku University, and colleagues have found that LiHMDS promotes the direct transformations of toluenes with ketones to produce stilbenes (pictured). The toluene substrate is used as a limiting reagent. LiHMDS is a more effective base for use in this reaction compared with other amide bases, such as NaHMDS and KHMDS, or alkoxide bases.
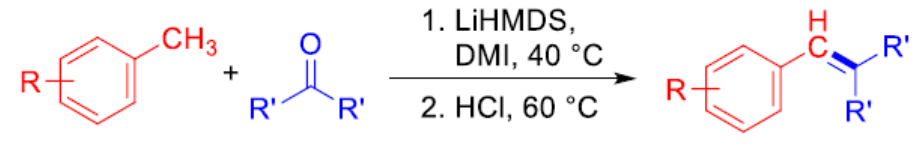
This system is compatible with a variety of functional groups (Cl, Br, OCF3, amide, alkenyl, alkynyl, SMe, and SPh) and gives a range of stilbene products. In addition, the reaction can be used for the transformation of less acidic (i.e., less reactive) substrates, such as 4-phenyltoluene and toluene itself, the latter of which is a cheap and abundant feedstock.
- LiHMDS‐mediated deprotonative coupling of toluenes with ketones,
Masanori Shigeno, Akihisa Kajima, Eito Toyama, Toshinobu Korenaga, Hiroyuki Yamakoshi, Kanako Nozawa-Kumada, Yoshinori Kondo,
Chem. Eur. J. 2022.
https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.202203549