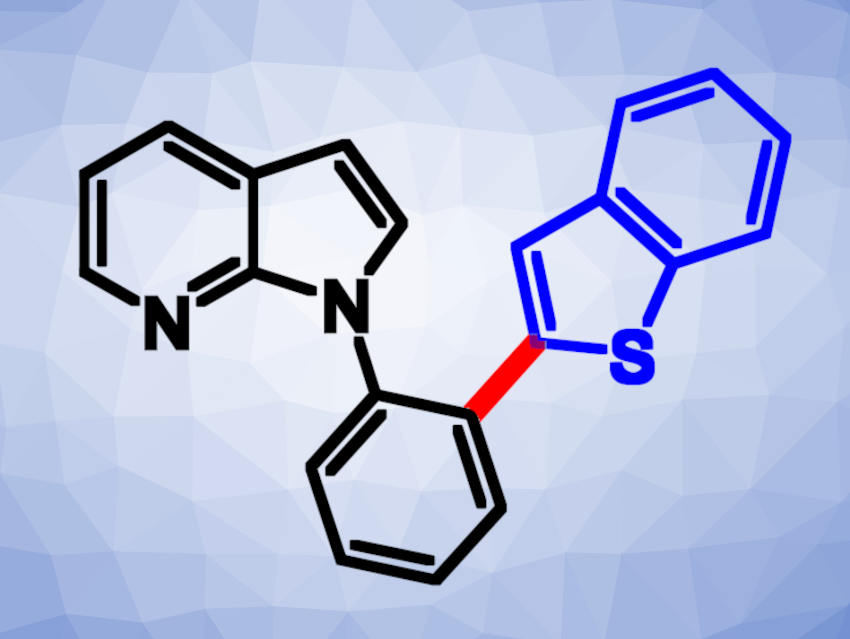
7-Azaindole units are found, e.g., in pharmaceutically active molecules and natural products, where they can serve as bioisosteres of indole units (i.e., chemically similar groups that produce similar biological properties). For example, 7-azaindole groups are present in drugs such as vemurafenib or decernotinib. New methods for the synthesis of 7-azaindole derivatives could, thus, be useful.
Yan-Jun Xu, Sichuan Normal University, China and colleagues have developed a rhodium-catalyzed crossdehydrogenative coupling (CDC) reaction of N-phenyl-7-azaindoles with thiophene derivatives to obtain new 7-azaindole derivatives (general reaction pictured below). The team used [Cp*RhCl2]2 as the catalyst, Ag2O as an oxidant, AgSbF6 as an additive, and MeOH as the solvent. The reactions were performed at 120 °C under an air atmosphere.
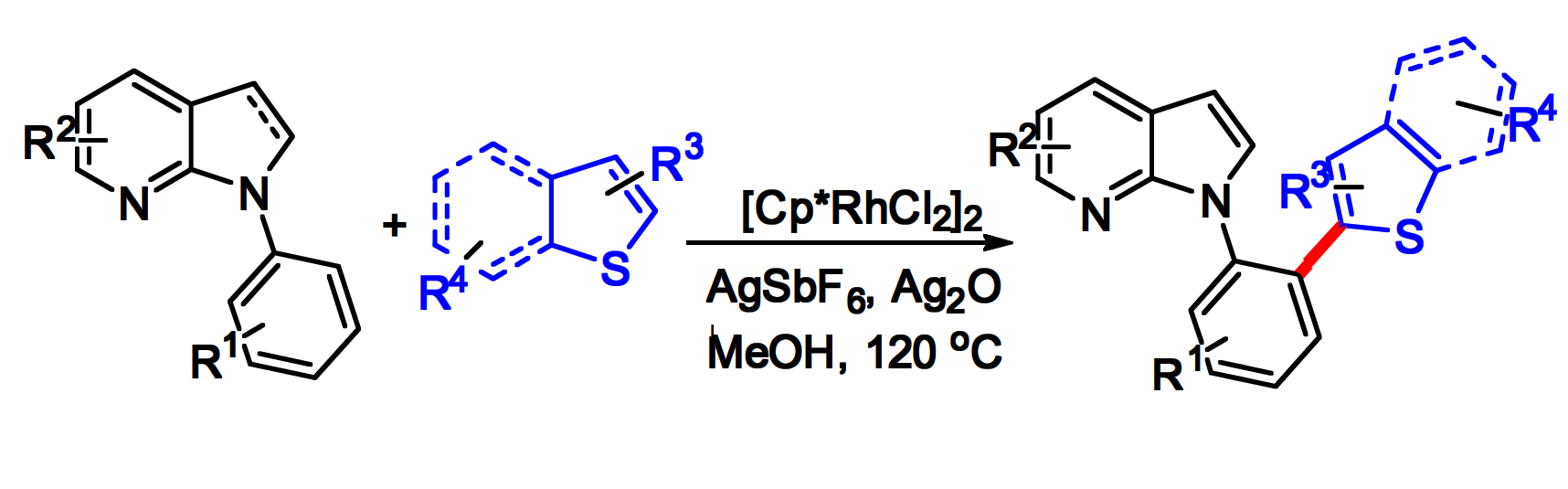
Under these conditions, a variety of N-phenyl-7-azaindoles were reacted with a range of thiophenes or benzothiophenes, and the desired products were obtained in moderate to good yields. The team was able to perform the reaction on a gram scale. The researchers propose a reaction mechanism that involves the generation of a six-membered rhodacycle intermediate via C–H activation at the N-phenyl-7-azaindole derivative, followed by coordination of the thiophene and C–H bond cleavage. A reductive elimination then releases the product and the catalyst is regenerated by oxidation.
- Rh(III)‐Catalyzed Cross Dehydrogenative Coupling of N‐Phenyl Substituent with Thiophenes,
Wen-Yi Wei, Zi-Rong Gong, Xin-Yu Chai, Yan-Jun Xu, Lin Dong,
Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2023.
https://doi.org/10.1002/ejoc.202300294