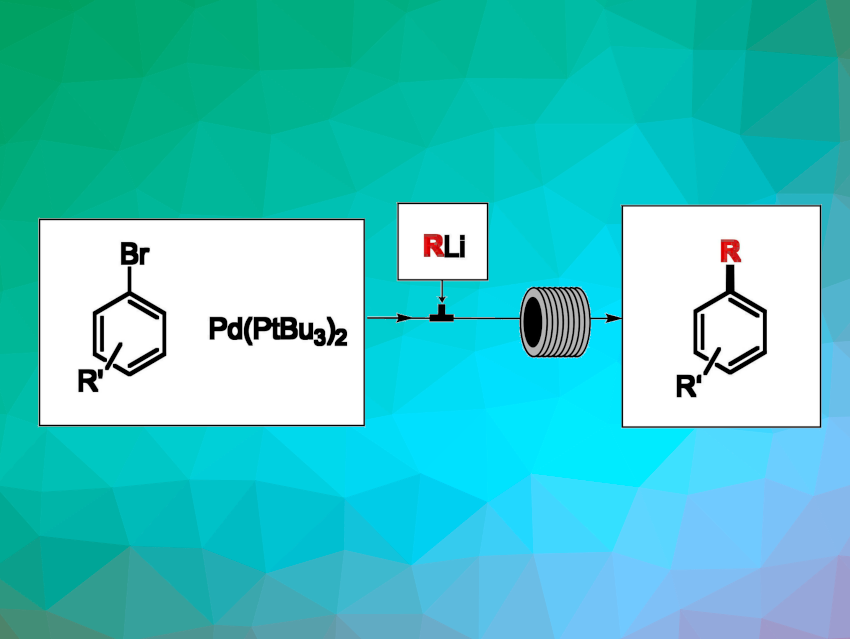
The use of readily available and relatively inexpensive organolithium reagents in Pd-catalyzed cross-coupling reactions is an attractive option for the preparation of organic compounds. However, the large-scale application of organolithium compounds has remained challenging due to their high reactivity. Continuous flow technologies can allow the handling of hazardous chemicals in a safer way and, thus, may offer a solution to this problem.
Maurizio Benaglia, Università degli Studi di Milano, Milan, Italy, and colleagues have developed an efficient continuous-flow protocol for Pd-catalyzed cross-coupling reactions of organolithium reagents with aryl bromides under aerobic conditions. The team first studied a model reaction between n-hexyllithium and 4-bromoanisol in a coil reactor, using Pd[P(tBu)3]2 as a catalyst with a 2.5 mol% loading and obtaining the desired product in a yield of 67 %. The researchers found that the catalyst loading could be lowered to 0.5 mol% while retaining a yield of 50 %.
Using optimized conditions, different organolithium reagents were reacted with a range of substituted aryl bromides, including polycyclic aromatic compounds and heteroarenes, leading to high yields in just 40 s residence time. The reaction was successfully scaled up and could also be applied to the synthesis of a class of lysine and arginine methyltransferase inhibitors used for the treatment of cancer.
- In Continuo Pd‐Catalysed Cross Coupling Reactions of Organolithium Reagents with Aryl Bromides under Aerobic Conditions,
Jacopo Brucoli, Davide Gariboldi, Alessandra Puglisi, Sergio Rossi, Vito Capriati, Maurizio Benaglia,
Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2024.
https://doi.org/10.1002/ejoc.202301289