Multicomponent reactions can combine three or more reagents into one desired product. This can be useful, e.g., in drug development to obtain a range of structurally diverse drug candidates by varying the components. Isocyanides are often used in multicomponent reactions, and there are examples of transition-metal-catalyzed reactions that involve a nitrene transfer using azides and isocyanides, giving carbodiimides (R–N=C=N–R’). This usually requires catalysts based on expensive noble metals. Cobalt could be a useful, abundant alternative.
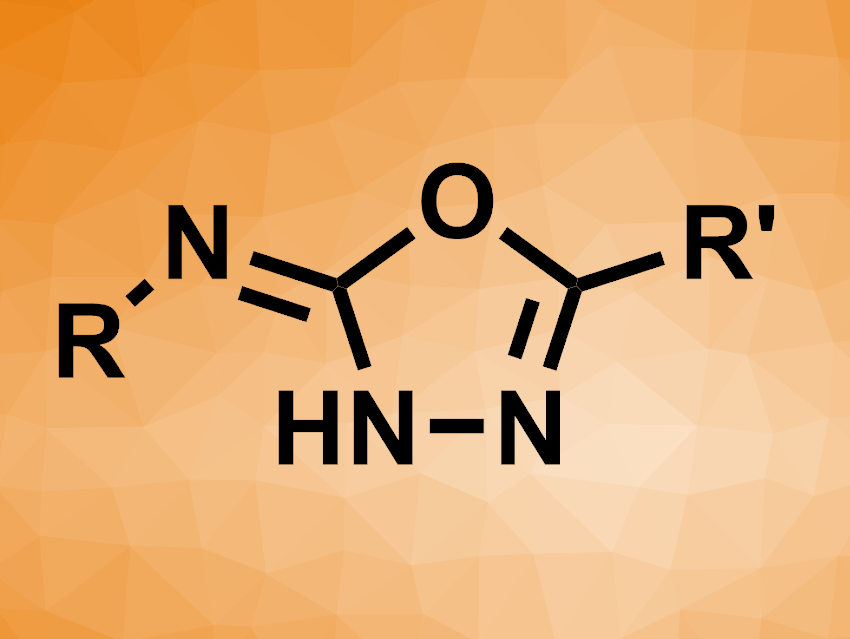
Jordy M. Saya, Romano V. A. Orru, Maastricht University, The Netherlands, Bert U. W. Maes, University of Antwerp, Belgium, and colleagues have developed a cobalt(II)-mediated three-component synthesis of 1,3,4-oxadiazol derivatives (general product structure pictured) from sulfonyl azides, N-isocyaniminotriphenylphosphorane (NIITP), and carboxylic acids. The team reacted different arene- or alkanesulfonyl azides with a broad range of aliphatic carboxylic acids and NIITP, using CoCl2 as a mediator and MeCN as the solvent at 60 °C. Catalytic amounts of CoCl2 only promoted the reaction with the desired selectivity when sterically hindered carboxylic acids were used; the team used a stoichiometric amount for other cases.
The desired 5-substituted-N-sulfonyl-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2(3H)-imines were obtained in yields of 22–82 %, depending on the substrates. The team proposes a reaction mechanism that involves the in-situ generation of a carbodiimide via a nitrene transfer, followed by addition of the carboxylic acid. Finally, an intramolecular aza-Wittig reaction gives the product. The products can be converted to 1,3,4-oxazol-2-amines, which can be used in further transformations.
- A Cobalt Mediated Nitrene Transfer aza-Wittig Cascade Reaction To Access 1,3,4-Oxadiazole Scaffolds,
Daniël S. Verdoorn, Prabhat Ranjan, Tim de Reuver, Elwin Janssen, Christophe M. L. Vande Velde, Jordy M. Saya, Bert U. W. Maes, Romano V. A. Orru,
Org. Lett. 2023.
https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.orglett.3c00959