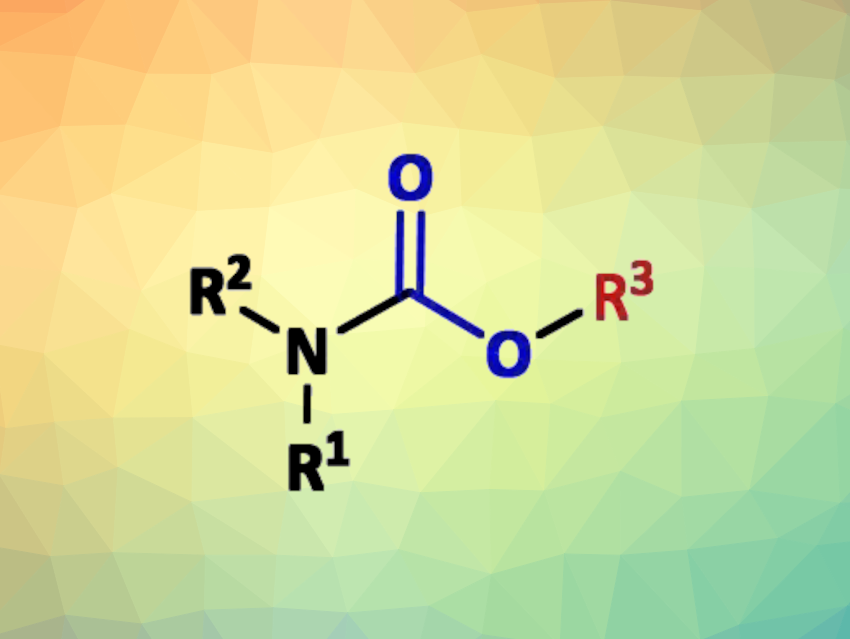
Organic carbamates are useful synthetic intermediates and widely used in industry. They are commonly prepared by the addition of alcohols to isocyanates or by reacting amines with alkyl chloroformates. Isocyanates and chloroformates are mainly prepared using toxic phosgene and derivatives. Most alternative methods, however, still employ expensive reagents/catalysts or need high pressures and temperatures.
Antonio C. B. Burtoloso and Jorge A. M. Vargas, University of São Paulo, Brazil, have developed a practical protocol for the synthesis of organic carbamates via the well-established three-component coupling between CO2, amines, and alkyl halides. The process operates under mild reaction conditions (1 atm of CO2, room temperature) and uses a polymer-supported base, i.e., 1,8-diazabicyclo[5.4.0]undec-7-ene on polystyrene (PS-DBU), which can be recovered and reused. The reaction is performed in a one-pot manner with no need for classical purification steps.
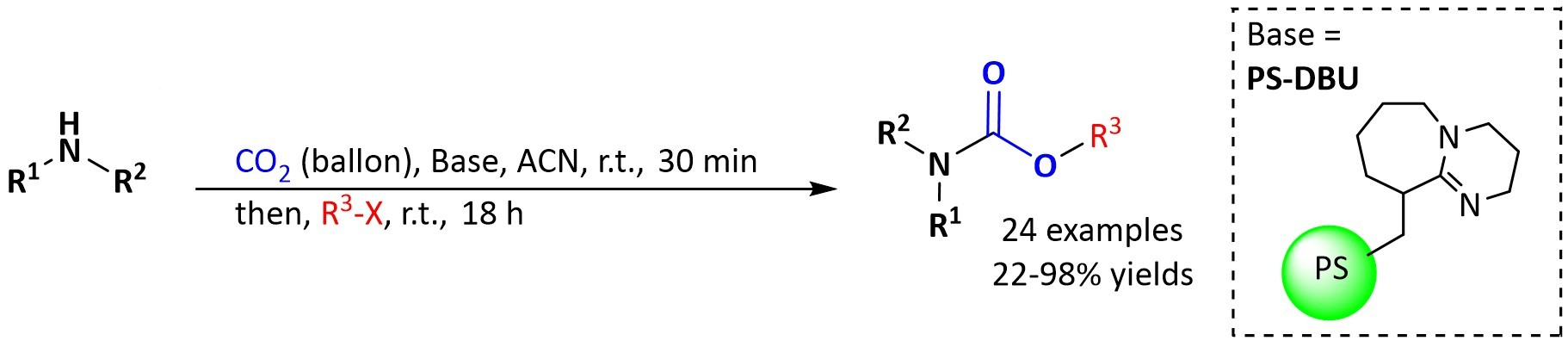
Different carbamates were obtained in moderate to good yields after a simple filtration followed by solvent evaporation. The reaction tolerates a range of amines and alkyl halides. PS-DBU could be recovered and reused several times with high carbamate yields. This protocol is a useful approach to the synthesis of carbamates and combines efficiency, a good substrate scope, and the potential for catalyst recycling.
- CO2‐Based Carbamate Synthesis Utilizing Reusable Polymer‐Supported DBU,
Jorge Andrés Mora Vargas, Antonio C. B. Burtoloso,
ChemSusChem 2023.
https://doi.org/10.1002/cssc.202300936