Proton Batteries
Proton batteries are an innovative and environmentally friendly type of battery in which charge is carried by protons, which are positively charged hydrogen ions. A team of researchers has developed organic sulfonamides as a robust and flexible material for cathodes in these batteries. Sulfonamide cathodes also achieve a higher output voltage than conventional cathodes.
In the constant search for alternatives to lithium-ion batteries, proton batteries are proven to have great potential. Rather than storing charge in the form of lithium ions, they transfer light, highly mobile protons, instead. As a result, this type of battery does not require the environmentally harmful and unsustainable mining of lithium. In addition, the mobile protons help achieve significantly shorter charging times than for other battery types.
Despite these advantages, the performance of the electrodes in proton batteries still requires improvement. To date, the cathodes (positive electrodes) were only able to achieve a fairly low output voltage, insufficient for most applications.
Sulfonamides Make Robust Cathode Material for Proton Batteries
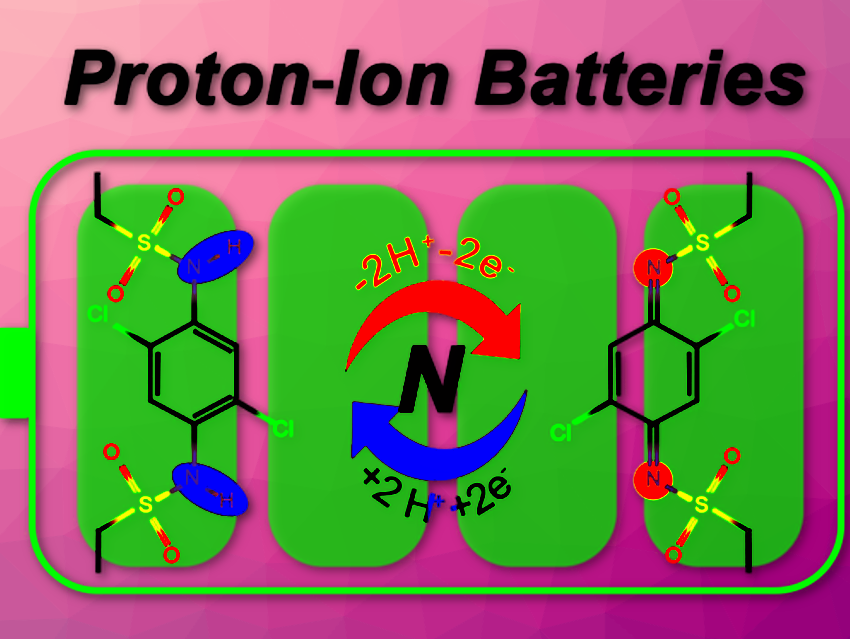
Bingan Lu and his team, Hunan University, Changsha, China, have improved this voltage by replacing the chemicals making the cathode material. Instead of organic carbonyl compounds or cyanide-based pigments, they used organic sulfonamides.
Rather than storing the protons at the oxygen atoms, as is the case in carbonyl compounds, sulfonamides store the protons at the nitrogen atom of the sulfonamide group. The researchers explain why this is beneficial: “the nitrogen atom has one more vacant site than the oxygen atom that can accept foreign electrons, making it much more tailorable.”
By attaching electron-withdrawing groups to the molecular scaffold, the researchers were able to increase the electric potential of the material. At 1 V, the output voltage achieved was 20 % higher than in the next-best materials, and the researchers are confident there is even further room for improvement with careful molecular design.
To assemble a complete proton battery, Lu and colleagues also developed a gel-like electrolyte which was adapted to the sulfonamide cathode material and enabled flexible construction. This malleable battery pack retained capacity over 600 charge/discharge cycles.
The advantage of using sulfonamides does not end with their chemical tailorability. Lu and colleagues report the new cathode material is also easy to manufacture, stable under standard environmental conditions, and virtually insoluble in water. The team highlights that sulfonamide-based proton batteries of this type do not contain any heavy metals and consist of non-toxic organic compounds, so they are readily recyclable.
- High-Potential Cathodes with Nitrogen Active Centres for Quasi-Solid Proton-Ion Batteries,
Dongyang Shen, Apparao M. Rao, Jiang Zhou, Bingan Lu,
Angewandte Chemie International Edition 2022.
https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202201972