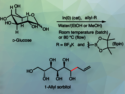
Phenol units are found in numerous natural products and pharmaceutically active compounds. In general, boronic acids and boronic esters can be valuable precursors for the synthesis of phenols and aliphatic alcohols. Photochemical protocols can be useful for this type of transformation.
Christoforos Kokotos, National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, Greece, and colleagues have developed a catalyst-free protocol for the hydroxylation of boronic acids and esters, utilizing atmospheric oxygen as the oxidation agent. The team used UV-A light to trigger the excitation of a complex between the boronic acid substrate and N,N’-diisopropylethylamine (DIPEA). The reactions were performed in acetonitrile at room temperature under air.
The photochemical protocol has been used for the transformation of various aryl and alkyl boronic acids and esters, giving the respective phenol or alcohol in good yields. The method has a broad substrate scope. The team proposes a reaction mechanism in which a superoxide anion is generated that reacts with the boronic acid to form the corresponding hydroxy derivative via a hydrogen-atom transfer, a rearrangement, and hydrolysis.
- UVA‐Light Promoted Catalyst‐Free Photochemical Aerobic Oxidation of Boronic Acids,
Petros L. Gkizis, Constantinos T. Constantinou, Christoforos G. Kokotos,
Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2023.
https://doi.org/10.1002/ejoc.202300898
![Synthesis of [c2]Daisy Chains via Mechanochemistry](https://www.chemistryviews.org/wp-content/uploads/2025/04/202504_RotaxanesWithSolidStateMechanochemistry-125x94.png)