The greenhouse gas carbon dioxide can be a useful renewable C1 source. Biomass can also serve as a carbon source. Glucose, for example, can be converted to various value-added chemicals. Using both CO2 and glucose as carbon sources in a reaction, thus, is an interesting research target. Carboxylic acids, for example, are important compounds and could be the targets of such a reaction.
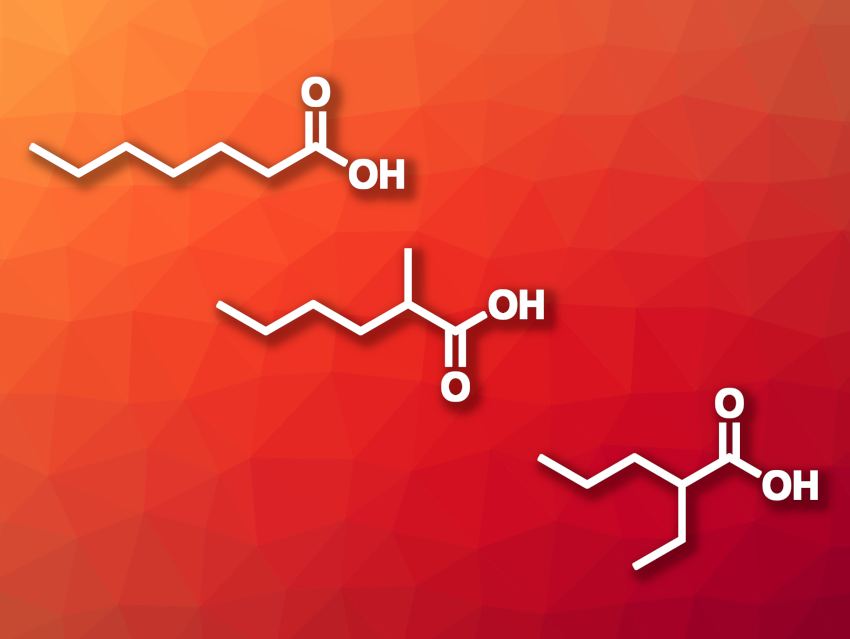
Qingli Qian, Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Huairou National Comprehensive Science Center, Beijing, China, Buxing Han, Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Sciences, Huairou National Comprehensive Science Center, University of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, and East China Normal University, Shanghai, and colleagues have developed a method for producing carboxylic acids via a reaction of saccharides with CO2 and H2. The team used Rh(acac)(CO)2 as the catalyst and I2 as a promoter. The reactions were performed in a mixture of acetic acid and water as the solvent at 160 °C. Glucose as a model substrate gave mostly C7 products, such as heptanoic acid, 2-methylhexanoic acid, and 2-ethylpentanoic acid (pictured).
Using 13CO2 labeling experiments, the team confirmed that the C atom in the carboxyl group of the acid stemmed from CO2. The team proposes that glucose first forms different C6 intermediates (ketones, olefins, etc.) under the reaction conditions, and that the CO2 is reduced to CO via the reverse water gas shift reaction. The CO then reacts with the C6 intermediates under rhodium catalysis to form the acyl group. The transformation can also be used for other saccharides with n carbon atoms, e.g., fructose, xylose, and glyceraldehyde, to give Cn+1 carboxylic acids.
- Synthesis of Carboxylic Acids from Saccharides, CO2, and H2,
Yang Li, Ying Wang, Yanru Zhang, Zhenpeng Wang, Junfeng Xiang, Juanjuan Han, Jun He, Longbo Zhang, Yanyan Wang, Qinglei Meng, Qingli Qian, Buxing Han,
ACS Catal. 2023.
https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.3c00374