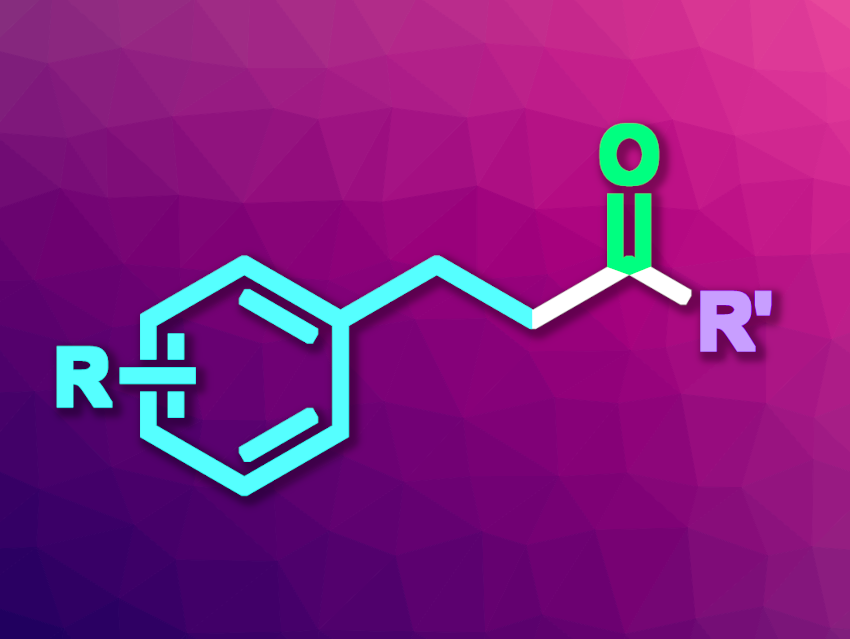
Ketones are useful products and intermediates in organic synthesis. They can be synthesized, for example, by transition-metal-catalyzed carbonylation reactions. Photochemical carbonylations are also interesting research targets, especially those leading to alkyl ketones.
Xiao-Feng Wu, Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Leibniz-Institut für Katalyse e.V., Rostock, Germany, and University of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, and colleagues have developed a method for a three-component photoredox-catalyzed carbonylative acylation of styrenes using Hantzsch esters and CO to give alkyl ketones (general product structure pictured). Hantzsch ester derivatives of the type HN[MeC=C(CO2Et)]2CHR’ were reacted with different styrenes under 60 bar CO in the presence of an iridum-based photocatalyst, using N,N-dimethylacetamide (DMAc) as the solvent. The reactions were performed under blue LED irradiation at 55–60 °C.
Under these conditions, the desired ketones were obtained in moderate to good yields. The team proposes a reaction mechanism in which the Hantzsch ester is oxidized by the activated photosensitizer under light irradiation to release an R’• radical. This radical reacts with CO to form an acyl radical, which can be added to the styrene derivatives. The resulting intermediate was reduced and protonated to give the target ketone. Overall, the work provides access to a range of alkyl ketones under mild conditions.
- Photoredox-catalyzed carbonylative acylation of styrenes with Hantzsch esters,
Qiangwei Li, Le-Cheng Wang, Zhi-Peng Bao, Xiao-Feng Wu,
Chem. Commun. 2024.
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4CC01293C