Stereoselective aldol additions are useful reactions in organic synthesis. Biocatalyzed processes for such reactions are interesting research targets. The use of biocatalysts can allow clean reactions with a low environmental impact.
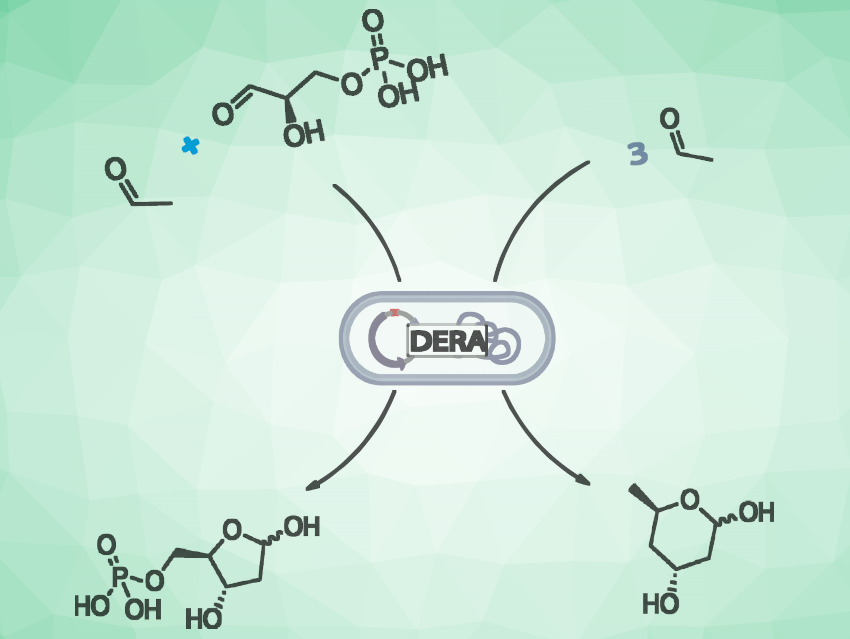
2-Deoxy-D-ribose-5-phosphate aldolase (DERA) naturally catalyzes the reversible formation of 2-deoxyribose-5-phosphate (DR5P) from D-glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate and acetaldehyde (pictured on the left). DR5P is a key intermediate in the biocatalytic preparation of deoxyribonucleosides and analogues with antiviral or antitumor activity. The enzyme can also use acetaldehyde as the sole substrate, resulting in a tandem aldol reaction, giving 2,4,6-trideoxy-D-erythro-hexapyranose, which cyclizes spontaneously (pictured on the right). This reaction is useful for the synthesis of the side-chain of statin-type drugs.
Elizabeth Lewkowicz, Universidad Nacional de Quilmes, Bernal, Argentina, and colleagues have found that a DERA variant from a strain of Pectobacterium atrosepticum (PaDERA) can be used in a recombinant whole-cell biocatalyst to synthesize DR5P and 2,4,6-trideoxy-D-erythro-hexapyranose. The team used different recombinant E. coli strains containing P. atrosepticum DERA.
The researchers selected E. coli BL21 (PaDERA C-His AA C49M) as the most appropriate whole-cell biocatalyst. It allows yields of 99 % for both desired products. Additionally, this biocatalyst can tolerate high concentrations of acetaldehyde (a common limitation of these enzymes), which could make it suitable for industrial applications.
- Synthetic activity of recombinant whole cell biocatalysts containing 2‐deoxy‐D‐ribose‐5‐phosphate aldolase from Pectobacterium atrosepticum,
Romina Fernández Varela, Ana Laura Valino, Eman Abdelraheem, Rosario Médici, Melisa Sayé, Claudio A. Pereira, Peter-Leon Hagedoorn, Ulf Hanefeld, Adolfo Iribarren, Elizabeth Sandra Lewkowicz,
ChemBioChem 2022.
https://doi.org/10.1002/cbic.202200147