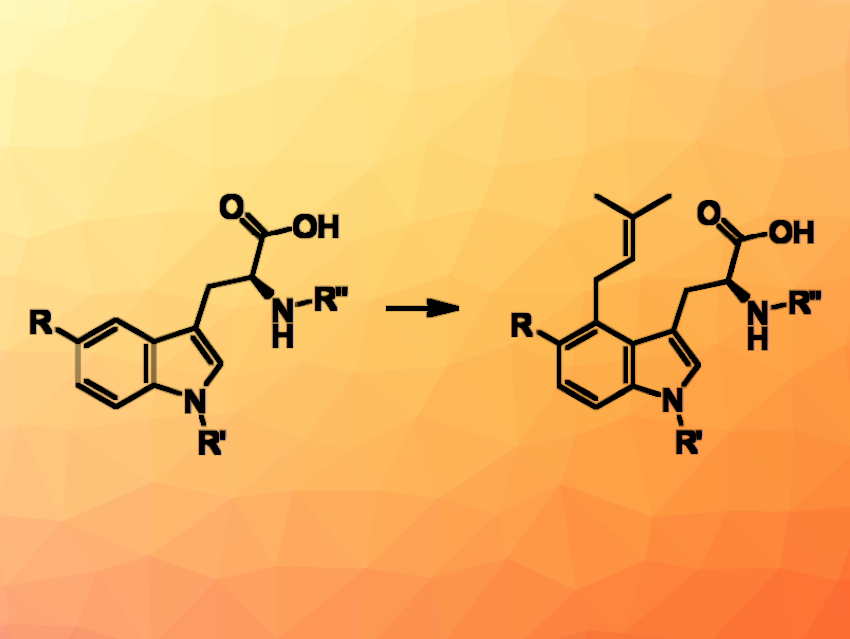
Regioselective C−C bond formation at aromatic non-pre-functionalized positions is a challenge for established chemistry. For instance, site-selective reactions with tryptophans require protection strategies. Biocatalysts may offer alternatives due to the possibility to position the two reaction partners in a very precise position relative to each other in the active site of the biocatalyst. C−C bond formation catalyzed by 4-dimethylallyltryptophan synthases (4-DMATSs) represents a possible tool to regioselectively synthesize C4-prenylated indole derivatives without site-specific preactivation and circumvent the need for protection groups as used in chemical synthetic approaches.
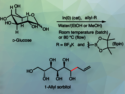
Bettina Eggbauer, University of Graz, Austria, and colleagues have set up a library of 4-DMATSs to produce a set of 4-dimethylallyl tryptophan and indole derivatives. Using wildtype enzymes from Aspergillus japonicus, Claviceps purpurea, and Trichophyton benhamiae as well as variants, various C5-substituted tryptophan derivatives as well as, for instance, N-methyl tryptophan were successfully prenylated in the C4 position with conversions up to 90 %. Even truncated tryptophan derivatives like tryptamine and 3-indole propanoic acid were regioselectively prenylated in position C4.
Docking studies with available 4-DMATS crystal structures allowed the generation of different variants, which showed improved acceptance (up to 5-fold) of C5-substituted tryptophan derivatives. The team also tested the feasibility to perform these reactions with selected tryptophan derivatives on a semi-preparative scale.
According to the researchers, the work demonstrates for the first time the potential of C4-prenylation of unprotected tryptophan derivatives for synthetic purposes at a reasonable substrate concentration. Such a single-step prenylation allows to shorten previously reported chemical synthesis routes to a single step and does not require preactivation or protecting groups. The reactions demonstrated successfully on a 100 mg scale that previously published multistep chemical synthetic sequences, e. g., of C4-prenylated tryptamine, can be reduced to a single step through the use of biocatalysis.
- Regioselective Biocatalytic C4‐Prenylation of Unprotected Tryptophan Derivatives,
Bettina Eggbauer, Joerg H. Schrittwieser, Bianca Kerschbaumer, Peter Macheroux, Wolfgang Kroutil,
ChemBioChem 2022.
https://doi.org/10.1002/cbic.202200311