The chirality of atropisomeric, or axially chiral, compounds is based on the hindered rotation around a σ bond due to the steric hindrance of neighboring groups. Often, this bond is a C–C bond connecting two aryl rings. Examples of this such as biaryl or binaphthyl derivatives are well-studied and widely used, e.g., as chiral ligands. “Hetero”-atropisomers based on C−O, C−S, or C−N bonds with hindered rotation are also known. In contrast to these systems, information about atropisomerism at C−B bonds in boron Lewis acids has remained limited so far.
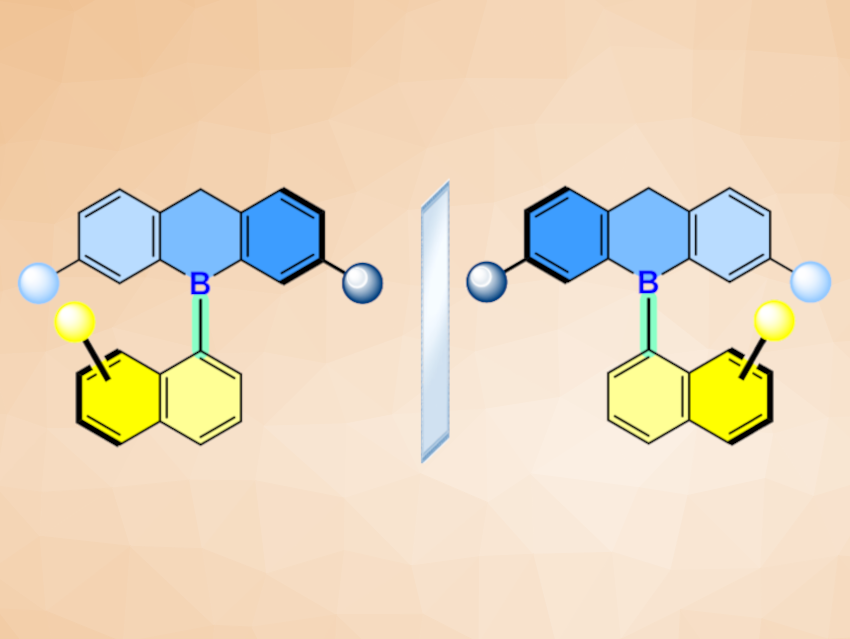
Thu-Hong Doan, Guillaume Berionni, University of Namur, Belgium, and colleagues have synthesized the first series of atropisomeric triarylboranes composed of a naphthyl rotor and a dihydro-9-bora-anthracenyl stator (simplified structure pictured), which create a C−B stereogenic axis. The team used crystallographic, kinetic, photophysical, and quantum chemical methods to study the mechanisms, rates, and barriers of diastereomerization and enantiomerization in these compounds.
The researchers synthesized the asymmetrical boranes starting from bis(2-bromophenyl)-methane derivatives, which were converted to bis(2-bromomagnesium aryl)-methane intermediates and then reacted with trimethylborate. The resulting boronates were reacted with naphthyl-based Grignard reagents to form the desired products.
The team found that the naphthalene units in several of the products are nearly perpendicular to the dihydro-9-bora-anthracene units, with interplanar angles of 77–90°. Chiral resolution using chiral high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) gave enantiopure triarylboranes with high configurational stability. Interestingly, the atropisomerical behavior of the synthesized triarylboranes can be controlled by a Lewis base. This is due to the formation of a Lewis acid/base adduct at the boron atom, which facilitates rotation around the C−B stereogenic axis by changing the structure around the B atom to avoid steric interactions between the two subunits.
- Atropisomerism in Triarylboranes: Lewis Base Assisted Rotation at C−B Stereogenic Axis in Asymmetrical Boron Lewis Acids,
Thu-Hong Doan, Aurélien Chardon, Nicolas Vanthuyne, Tárcius N. Ramos, Nikolay Tumanov, Luca Fusaro, Muriel Albalat, Laurent Collard, Johan Wouters, Benoît Champagne, Guillaume Berionni,
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2025.
https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202421931