Capturing carbon dioxide, e.g., from the flue gas produced by power plants using fossil fuels, is an important part of mitigating emissions and mitigating climate change. One approach to this is the use of aqueous amine solutions, which capture CO2 either via the formation of an ammonium carbamate under dry conditions or via the formation of an ammonium bicarbonate and/or carbonate under humid conditions. However, the amines used for this can have drawbacks such as toxicity, corrosiveness, and instability under the conditions in CO2 “scrubbers”.
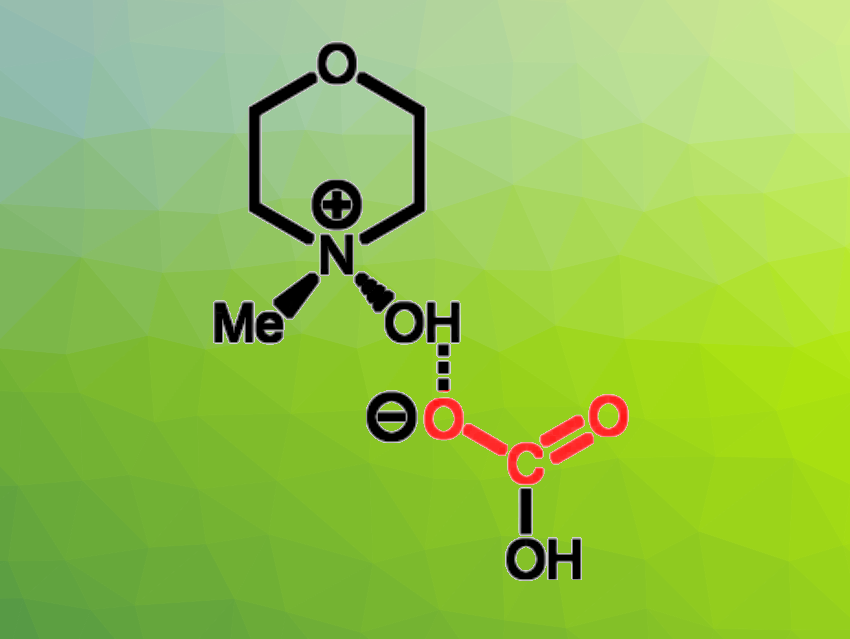
Tristan H. Lambert, Phillip J. Milner, Cornell University, Ithaca, NY, USA, have found that tertiary amine N-oxides can also be used to remove CO2 from waste gas streams such as flue gas. The team used 4-methylmorpholine N-oxide (MMNO), which can form a hydrogen-bond-stabilized HCO3– species (pictured) with CO2 under humid conditions.
The researchers found that the inexpensive MMNO shows good stability under the necessary conditions for carbon capture, as well as good CO2 uptake. In contrast to the amines used for this, the compound is nontoxic and noncorrosive. While the amines require high temperatures for regeneration after capture, MMNO releases CO2 at about 65 °C in a simulated temperature swing process. Overall, the work demonstrates the promise of trialkylamine N-oxides such as MMNO for use in carbon capture technologies.
- Harnessing Oxidized Amines as Robust Sorbents for Carbon Capture,
Sijing Meng, Tristan H. Lambert, Phillip J. Milner,
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2025.
https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.4c16764
Also of Interest
Interview: Chemical Solution to the CO2 Problem
Omar Yaghi discusses COF-999’s CO₂-adsorbing ability, its climate change potential, his research in reticular chemistry, and chemistry’s role in addressing societal challenges like water scarcity