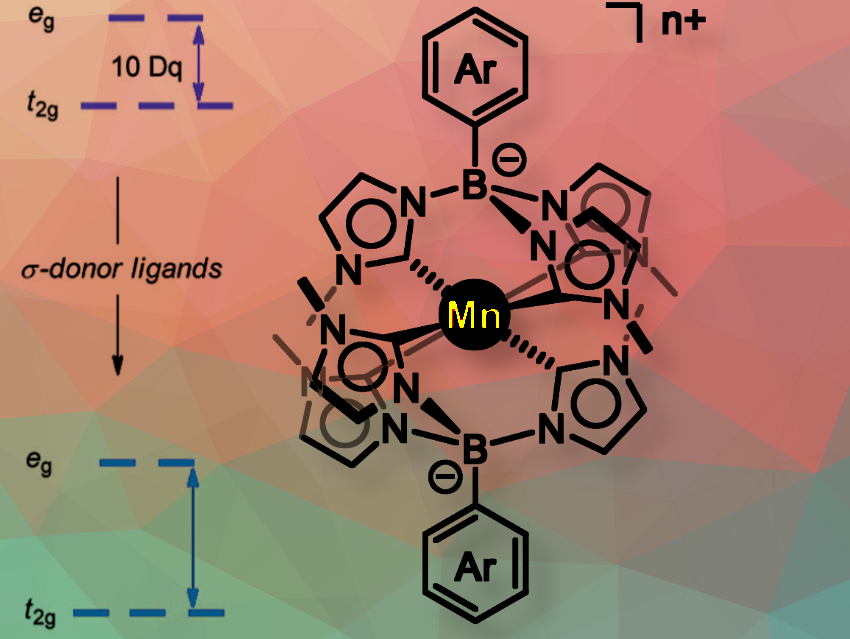
Manganese complexes are promising photocatalysts due to their eco-compatibility, versatile valence states, and multiple electronic excitation capabilities, though limited by poor visible light response and short excited-state lifetimes.
Yu-Mei Lin, Xiamen University, China, and colleagues have developed manganese complexes with boron-containing N-heterocyclic carbene (NHC) ligands. These complexes have long excited state lifetimes, up to microseconds for Mn(IV) and nanoseconds for Mn(III), and strong photoredox properties, allowing efficient and selective cross-coupling under mild conditions. They have strong oxidative and reductive capabilities in their excited states, which significantly enhances the efficiency of photoredox activation.
The team validated the effectiveness of the manganese complexes as photoredox catalysts by their successful application in cross-couplings between diverse arenes and aryl bromides. These complexes are highly efficient for direct, site-selective cross-couplings at low catalyst loadings (0.5 mol%). The team also successfully applied them to various other photochemical transformations, including reductive cross-couplings for the formation of C−P, C−B, C−S, and C−Se bonds, and oxidative couplings for the formation of C−N bonds.
The proposed mechanism involves the photoexcitation of the Mn(III) complex, followed by a single-electron transfer to the aryl bromide to give an aryl radical and a bromide ion. The resulting Mn(IV) complex absorbs visible light again, and its photoexcited state oxidizes the arene to give a second radical. Radical recombination then leads to the desired product.
The system is compatible with a wide variety of substrates, including very electron-rich arenes such as 1,3-dimethoxy-5-methylbenzene and extremely electron-poor substrates such as 1,2,4-trifluorobenzene and 2,6-difluoropyridine, which have rarely been used in conventional transition-metal-catalyzed cross-coupling reactions. According to the researchers, their work highlights the unique photoredox properties and remarkable catalytic flexibility of these manganese complexes, showcasing their potential in photochemical synthesis and green chemistry.
- Manganese Complexes with Consecutive Mn(IV)Mn(III) Excitation for Versatile Photoredox Catalysis.
Tao Huang, Pangang Du, Xiuliang Cheng, Yu-Mei Lin,
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024.
https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.4c07084