Surgeries often require anticoagulants like heparin to prevent thrombosis (the formation of blood clots). Heparin is used to inhibit antithrombin-II activity, a protein that helps regulate blood clotting. However, restoring normal blood coagulation functions after surgery is becoming a challenge. Protamine is the only heparin antagonist approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). It works by binding to heparin, forming a complex that neutralizes its ability to inhibit blood clotting. However, Protamine has significant side effects and only partially neutralizes some forms of heparin such as low molecular weight heparins (LMWHs) and unfractionated heparin (UFH), which are commonly used anticoagulants. This limitation makes it difficult to fully reverse the anticoagulant effect and safely restore normal blood clotting after surgery.
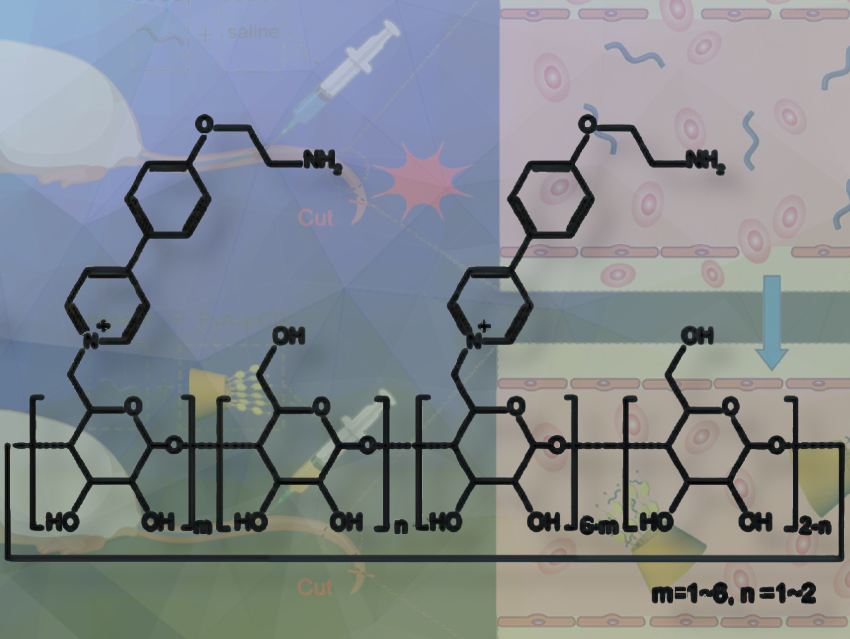
Yong Chen, Yu Liu, and colleagues, Nankai University, Tianjin, China, have synthesized an aminoethoxy-phenyl-pyridinium modified γ-cyclodextrin (PyA-γ-CD) as an antidote for heparin antagonism. They synthesized PyA-γ-CD by reacting 4-hydroxyphenylboronic acid, 4-bromopyridine hydrochloride, and potassium carbonate in DMF/H₂O with Pd(PPh₃)₄ to yield 4-(pyridine-4-γl)phenol. This was converted to tert-butyl(2-(4-(pyridine-4-γl)phenoxy)ethyl)carbamate with potassium carbonate and 2-(Boc-amino)-ethyl bromide in DMF at room temperature. Reacting this compound with octakis-(6-iodo-6-deoxy)-γ-cyclodextrin in DMF, followed by deprotection with HCl, yielded PyA-γ-CD.
The team found that PyA-γ-CD has a high binding affinity for heparin anticoagulants via multivalent interactions. It is believed that the abundant positively charged pyridinium units and the partially protonated amino groups of PyA-γ-CD interact electrostatically with the negatively charged sulfonated and carboxylate anions on heparin. Moreover, an additional interaction might be through intermolecular hydrogen bonds between the unprotonated amino groups of PyA-γ-CD and heparin.
Compared to Protamine, PyA-γ-CD shows nearly complete neutralization activity for unfractionated heparin (UFH) and effectively neutralizes three LMWHs (dalteparin (Dalte), enoxaparin (Enoxa), and nadroparin (Nadro)) with a broader therapeutic dose range, while showing low hemolysis and high cell viability at a cellular level. PyA-γ-CD can completely reverse bleeding caused by anticoagulant overdose, with no adverse effects observed in vivo. According to the researchers, PyA-γ-CD is a promising biocompatible and highly efficient anti-heparin coagulant.
- Polycationic γ-Cyclodextrin with Amino Side Chains for a Highly Efficient Anti-Heparin Coagulant,
Wen-Jin An, Zhuo Lei, Xiao-Yong Yu, Chu-Han Liu, Chen Zhang, Yong Chen, Yu Liu,
Advanced Health Materials 2025.
https://doi.org/10.1002/adhm.202404357