Genome editing has revolutionized agriculture, producing innovations like high-oleic soybeans, low-pungency mustard greens, and high Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) tomatoes, and has a great potential to enhance agricultural sustainability. Traditionally, the SpCas9 nuclease (about 1350 amino acids) has been widely used, but its large size complicates effectively delivering the nuclease into cells, especially through viral vectors. Smaller nucleases improve delivery efficiency and facilitate the creation of fusion proteins, which combine different protein domains to expand genome engineering capabilities.
Mirza J. Baig and Kutubuddin A. Molla, both ICAR-National Rice Research Institute, Cuttack, India, and colleagues have developed a miniature plant genome editor that is only one-third the size of Cas9. This new genome editor protein is derived from the transposon-associated TnpB of Deinococcus radiodurans, a bacterium known for its extraordinary resistance to radiation and extreme environmental conditions. The bacterium’s robust DNA repair mechanisms is of interest for various aplications.
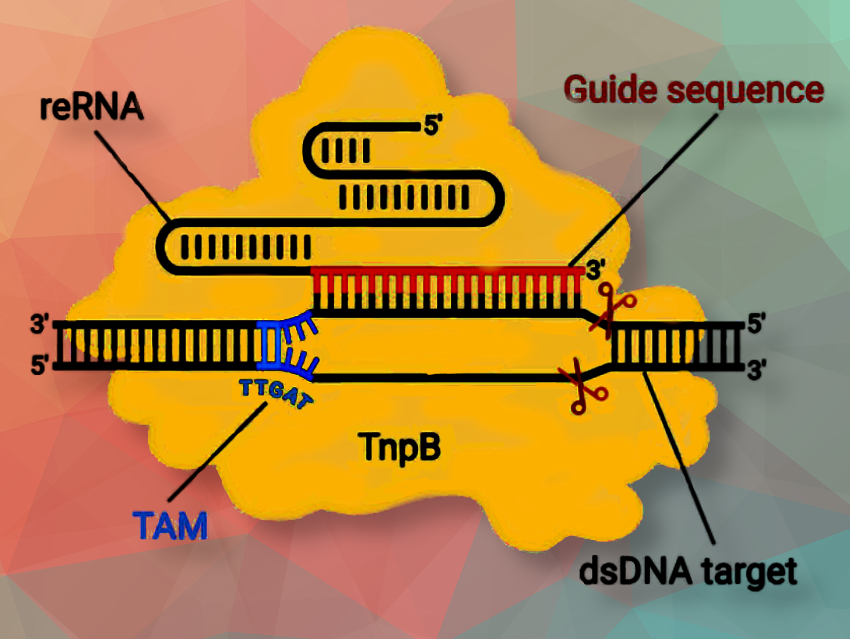
The miniature plant genome editor uses TnpB, guided by RNA to specific DNA targets in plant cells, to make precise cuts. Both Cas9 and TnpB need a specific DNA sequence next to their target site to work. For Cas9, this sequence is called a protospacer adjacent motif (PAM). For TnpB, it’s called a transposon-associated motif (TAM). The difference in these required sequences allows TnpB to reach and edit parts of the genome that Cas9 cannot, giving scientists more options and flexibility in genome editing.
The team optimized the editor by improving the expression system for TnpB and its RNA guide, significantly boosting its efficiency to 33.58%, and demonstrated its effectiveness in editing multiple genes in both monocot rice and dicot Arabidopsis.
Additionally, the team demonstrated that TnpB could be adapted for other tasks, such as activating genes and making precise changes to DNA without cutting it. This versatility makes TnpB a promising tool for various genetic modifications in plants.
- A miniature alternative to Cas9 and Cas12: Transposon-associated TnpB mediates targeted genome editing in plants,
Subhasis Karmakar, Debasmita Panda, Sonali Panda, Manaswini Dash, Romio Saha, Priya Das, S. P. Avinash, Justin Shih, Yinong Yang, A. K. Nayak, Mirza J. Baig, Kutubuddin A. Molla,
Plant Biotechnology Journal 2024.
https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.14416