Researchers led by Alexander N. Grechkin have discovered new oxylipins in the brown alga Ectocarpus siliculosus. By expressing the protein CYP5164A3 in Escherichia coli and using soybean lipoxygenase to synthesize hydroperoxides, they found that the protein converts specific hydroperoxides into novel compounds called ectocarpins (A-D) and plasmodiophorols (A-C) [1]. The team also identified similar compounds in another organism, Plasmodiophora brassicae, using a related protein.
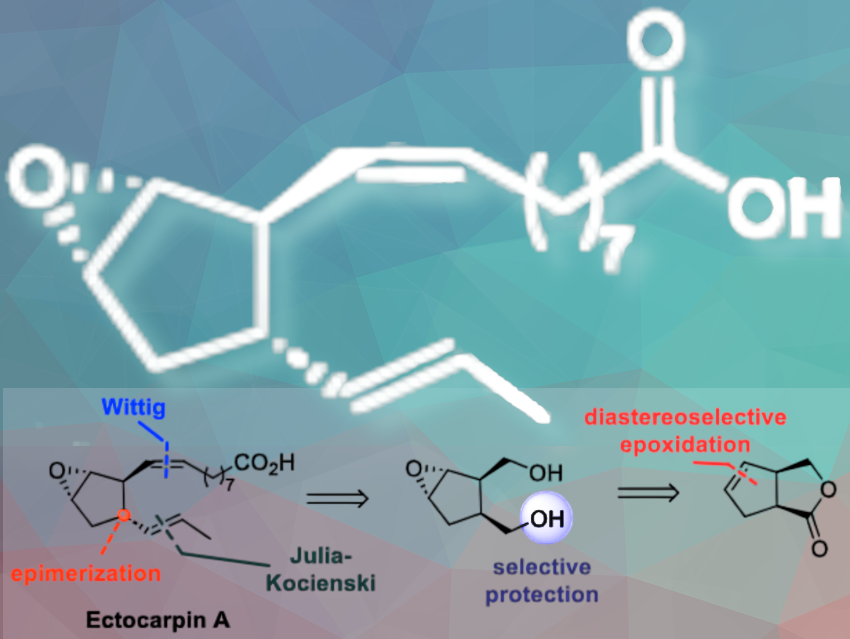
Camille Oger and colleagues, Université de Montpellier, CNRS, France, have achieved a fully enantioselective total synthesis of ectocarpin A (pictured above), a new oxylipin, in 12 steps starting from the chiral lactone tetrahydro-1H-cyclopentafuranone. Key transformations include the creation of the chiral tetrahydro-1H-cyclopentafuranone, a diastereoselective epoxidation, an enzymatic desymmetrization of a 1,4-diol, an epimerization, and both Wittig and Julia-Kocienski olefinations to build the carbon framework of Ectocarpin A.
The synthesis starts with the preparation of the chiral core and insertion of the first lateral chain. The final steps involve Julia-Kocienski olefination and saponification of the methyl ester, yielding ectocarpin A in 6% overall yield, corresponding to 79%per step of synthesis. The team purified the compound using semi-preparative HPLC, and confirmed its structure through comprehensive NMR characterization.
- Total Synthesis of Ectocarpin A,
Alexandre Guy, Thierry Durand, Camille Oger,
Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2025.
https://doi.org/10.1002/ejoc.202500381
[1] Y. Y. Toporkova, E. O. Smirnova, L. S. Mukhtarova, A. N. Grechkin, Lipoxygenase pathway in brown algae: The biosynthesis of novel oxylipins ‘ectocarpins’ by hydroperoxide bicyclase CYP5164A3 of Ectocarpus siliculosus, Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA – Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2022, 1867, 159205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbalip.2022.159205