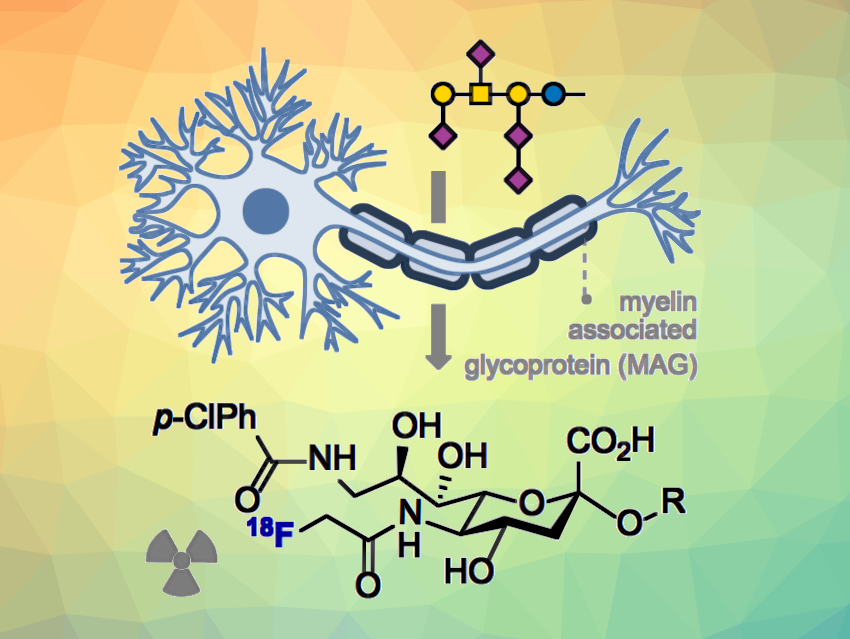
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an autoimmune disease that targets the central nervous system (CNS), causing damage to the myelin sheath, the protective layer of the nerve cell axons, and leaving axons vulnerable to injury. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is commonly used for diagnosis, but its accuracy is limited because it relies on imaging water molecules between the myelin layers instead of the myelin itself. This can make, e.g., inflammation or edema (excess fluid) look similar to MS lesions. Positron Emission Tomography (PET) offers a potential solution by using radiotracers that bind to myelin biomarkers for local resolution and quantification.
Andreas Faust, Ryan Gilmour, University of Münster, Germany, and colleagues have synthesized an 18F-PET radiotracer that is designed to have a high affinity towards myelin-associated glycoprotein (MAG). The sialic acid-derived tracer was prepared via a multistep sequence, starting with peracetylating a commercially available 5-neuaminic acid, followed by thioglycoside formation to introduce a protecting group. A selectively deprotected amide was then substituted with 2-(benzyloxy)acetyl chloride. Subsequent steps included a glycosylation, a Staudinger reaction, and an amide formation to obtain a precursor for radiolabeling. The final step involved installing the 18F label through displacement of a leaving group and global deprotection under ester hydrolysis conditions.
HPLC studies confirmed product characteristics, while in vitro stability tests in human and mouse blood serum showed that the radiotracer remained stable for at least one half-life (i.e., about 110 min). According to the researchers, these findings warrant further in vivo studies to evaluate the tracer’s MAG-binding affinity and blood-brain barrier permeability, which could ultimately advance diagnostic methods for MS.
- Design and Synthesis of a Sialic Acid-Derived Tracer for 18F-PET Multiple Sclerosis Imaging,
Kathrin Siebold, Lea Gobel, Christian Paul Konken, Andreas Faust, Rayn Gilmour,
Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2025.
https://doi.org/10.1002/ejoc.202401381