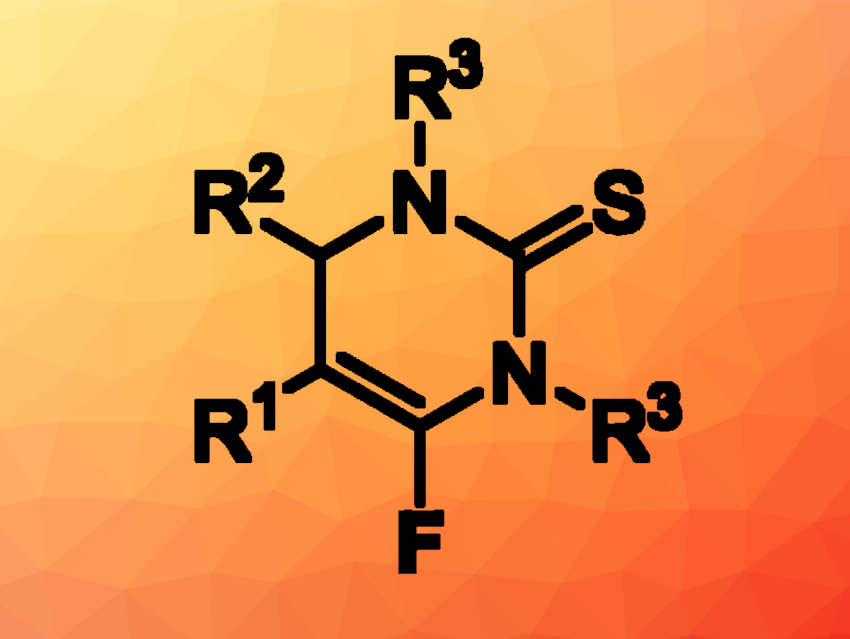
Dihydropyrimidine-2(1H)-thiones are heterocyles that are often found, e.g., in bioactive compounds. Derivatives that contain fluorine atoms can be interesting in pharmaceutical chemistry because fluorine substituents can be used to tune properties such as the lipophilicity and stability of drug candidates.
Chuanle Zhu, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou, and South China Agricultural University, Guangzhou, and colleagues have developed a method for the synthesis of 6-fluoro-3,4-dihydropyrimidine-2(1H)-thiones (general product structure pictured) via a chemoselective defluorinative [3+3] annulation of (trifluoromethyl)alkenes with thioureas. The team reacted a variety of (trifluoromethyl)alkenes with different thioureas in the presence of t-BuONa as a base, using N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF) as the solvent. The reactions were performed at room temperature.
Under these conditions, the desired fluorine-functionalized dihydropyrimidine-2(1H)-thiones were obtained in moderate to high yields. The reaction is transition-metal free and tolerates a range of functional groups. The researchers successfully performed it on a gram scale, obtaining the product in a yield of 86 %.
- Mild [3 + 3] Annulation of (Trifluoromethyl)alkenes with Thioureas Enabled by Chemoselective Defluorinative Amination: Synthesis of 6-Fluoro-3,4-dihydropyrimidine-2(1H)-thiones,
Rongbin Peng, Chuanle Zhu,
J. Org. Chem. 2025.
https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.joc.4c02479