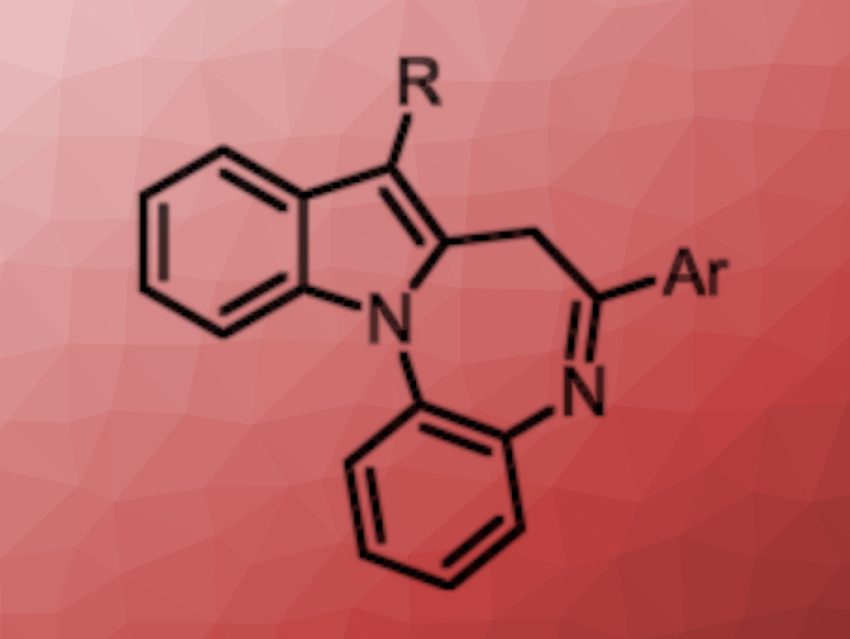
Benzodiazepines are a class of pharmaceutically active compounds. They affect the central nervous system and are used to treat anxiety, for example. Indole-fused benzodiazepines are one class of benzodiazepine derivatives used in drug discovery. Cascade reactions that allow the formation of multiple bonds in one step are interesting for the synthesis of such indole-fused diazepines.
Takahiko Akiyama, Gakushuin University, Tokyo, Japan, and colleagues have developed a method for the photocatalyzed synthesis of indole-fused benzodiazepines (general product structure pictured) via a cascade reaction. The team reacted different α-acetoxy aryl ketones with a variety of o-indoloanilines in the presence of 10-phenylphenothiazine (PTH) as a photocatalyst and Na2CO3 as a base. The reactions were performed in acetonitrile at room temperature under 370 nm LED light.
Under these conditions, the desired indole-fused benzodiazepines were obtained in moderate to high yields. The team proposes a reaction mechanism that involves a single-electron reduction of the α-acetoxy aryl ketone to generate an acyl radical. The radical undergoes an addition to the indole reaction partner, followed by a single-electron oxidation, deprotonation, and cyclodehydration to give the product. Overall, the protocol is efficient and environmentally friendly and provides access to benzodiazepines from readily available starting materials.
- Synthesis of Indole-Fused Benzodiazepine Derivatives by Photocatalyzed Cascade Reaction,
Tatsushi Oishi, Tatsuhiro Uchikura, Takahiko Akiyama,
Chem. Commun. 2025.
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4CC05755D