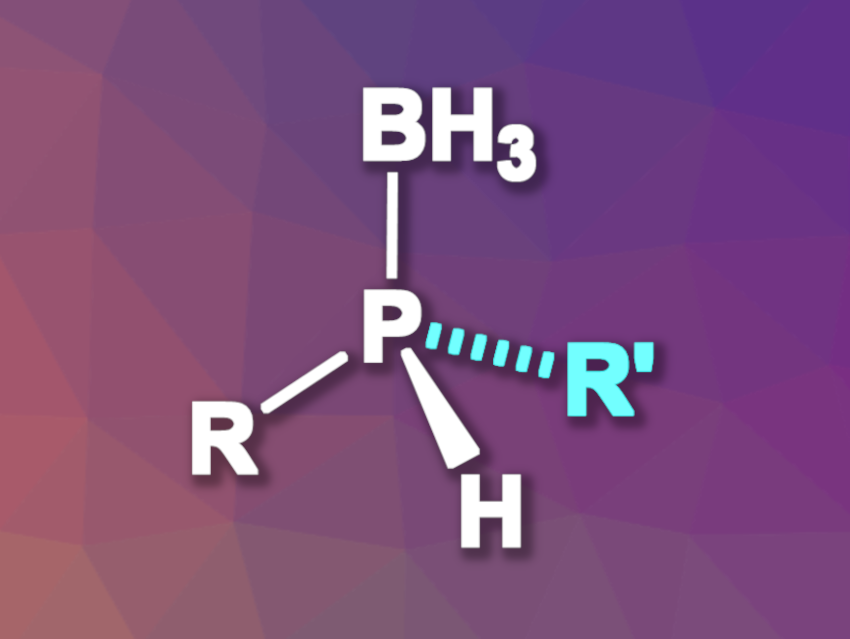
Compounds with stereogenic phosphorus centers can be useful, e.g., in pharmaceutical chemistry, agrochemistry, or as chiral ligands. However, they can be challenging to synthesize. Methods based on asymmetric catalysis that avoid a need for stoichiometric amounts of chiral reagents or chiral resolution can suffer, for example, from narrow substrate scopes.
Chuanyong Wang, Jiandong Guo, Yangzhou University, China, Wei-Liang Duan, Yangzhou University and Inner Mongolia University, Hohhot, China, and colleagues have developed a method for the nickel-catalyzed asymmetric alkylation of primary phosphines using alkyl halides, which gives P-stereogenic secondary phosphine-boranes (general product structure pictured) with high enantioselectivities. The method has a broad substrate scope. The team used a chiral PCP’ pincer nickel complex as the catalyst, diisopropylethylamine (iPr2NEt) as a base, and dichloromethane (DCM) as the solvent. The alkylation was followed by borane protection using BH3·SMe2. The reactions were performed at –78 °C to reduce the risk of racemization.
Under these conditions, the desired chiral phosphine-boranes were obtained in mostly high to excellent yields and with up to 99 % ee. As the alkyl halide reagent, the team used, for example, benzyl bromides, heterobenzyl bromides, allyl bromides, propargyl bromides, or α-bromo carboxylic acids. The products can be further transformed to give, for example, chiral tertiary phosphine-boranes. Overall, the work provides efficient access to both previously known and new P-stereogenic compounds.
- Nickel-Catalyzed Enantioselective Alkylation of Primary Phosphines,
Chuanyong Wang, Yuan-Hao Dai, Zheng Wang, Bin Lu, Wanxin Cao, Jing Zhao, Guoshun Mei, Qingliang Yang, Jiandong Guo, Wei-Liang Duan,
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024.
https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.4c10211