N-aryl amines are important compounds, e.g., in pharmaceutical chemistry and agrochemistry. They can be synthesized, for example, using copper-catalyzed C–N coupling reactions. The coupling of alkyl amines and aryl halides can, however, still be challenging. Finding suitable ligands for the catalysis of such reactions is key. Existing systems using anionic ligands can require a strong base, which limits the substrate scope. The coordination of deprotonated substrates or coordinating heterocycles in the reactants to the catalyst can also lead to catalyst deactivation.
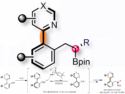
Stephen L. Buchwald, Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), Cambridge, USA, and colleagues have developed a copper-based catalytic system for the amination of base-sensitive aryl bromides. They used an anionic N,N‘-diarylbenzene-1,2-diamine ligand, along with NaOTMS (sodium trimethylsilanolate) as a weaker base. The team used CuI together with this ligand/base combination and dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) as the solvent to react aryl bromides containing different base-sensitive functional groups or coordinating heterocycles with primary or secondary amines. The reactions were performed at 24–70 °C.
Under these conditions, the desired amination products were obtained in mostly high to excellent yields. The work extends the scope of copper-catalyzed C–N coupling reactions. It is suitable for different base-sensitive substrates, including, for example, arenes functionalized with amides or enolizable ketones, as well as base-sensitive and coordinating heterocycles.
- Cu-Catalyzed Amination of Base-Sensitive Aryl Bromides and the Chemoselective N- and O-Arylation of Amino Alcohols,
Michael J. Strauss, Kaylee X. Liu, Megan E. Greaves, Jakob C. Dahl, Seoung-Tae Kim, Yong-Jin Wu, Michael A. Schmidt, Paul M. Scola, Stephen L. Buchwald,
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024.
https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.4c05246