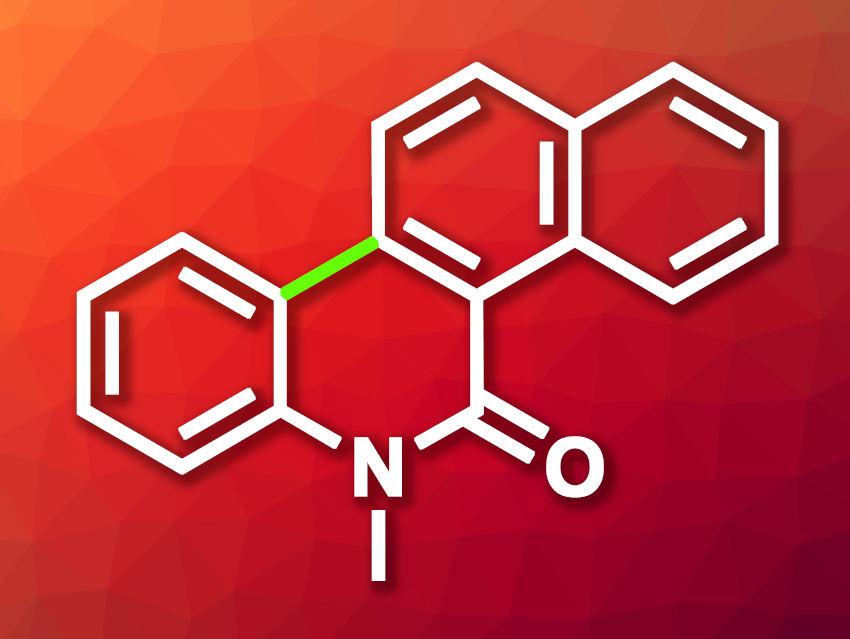
Dehydrogenative 6π photocyclization reactions can be useful tools for the synthesis of polycyclic aromatic systems. They can lead to, e.g., natural products or pharmaceutically active species. Benzophenanthridinone derivatives such as 6-methylbenzo[i]phenanthridin-5(6H)-one (pictured), for example, are interesting targets in medicinal chemistry.
Xiaoying Niu, Xiu-Long Yang, Hebei University, Baoding, China, Qing-Yuan Meng, Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Sciences and University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China, and colleagues have developed a method for the dehydrogenative 6π photocyclization of N-substituted naphthalene carboxamides that gives benzo[i]phenanthridin-5(6H)-ones. The team started from different N-phenyl-1-naphthamides, which were dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) and subjected to purple light irradiation (405–410 nm) at room temperature under air.
Under these conditions, without any photosensitizers or additives, a broad range of N-phenyl-1-naphthamides were cyclized to give the desired products in moderate to high yields. The reaction was successfully performed on a gram scale, giving a yield of 84 %. According to the team, DMSO serves as both solvent and oxidant in the transformation.
- Intramolecular Dehydrogenative Photocyclization of N-Phenyl-1-naphthamides,
Hao-Yuan Li, Xiaoying Niu, Shan-Shan Zhang, Shigang Shen, Qing-Yuan Meng, Xiu-Long Yang,
Org. Lett. 2024.
https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.orglett.4c01805