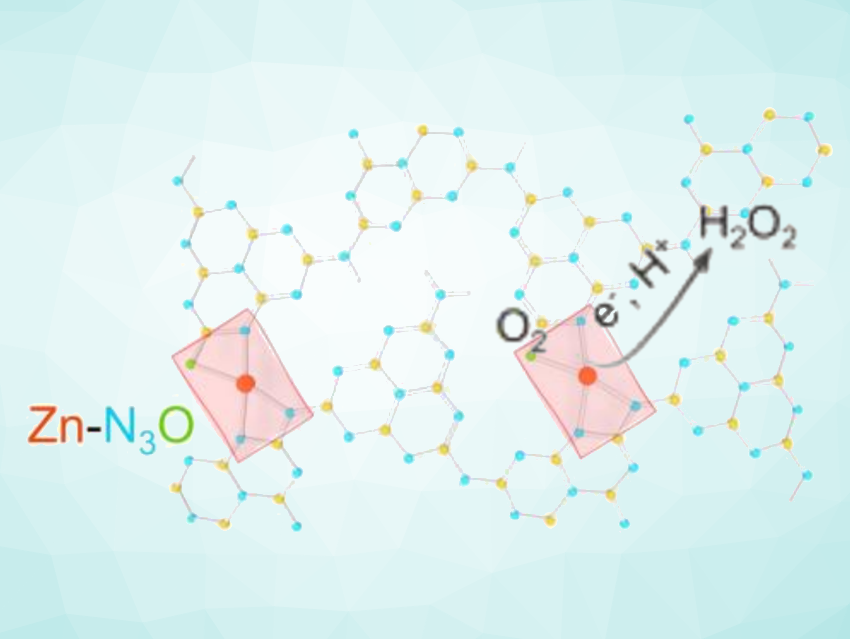
Hydrogen peroxide is widely used and can serve as an environmentally friendly oxidant. The traditional anthraquinone process for producing H2O2 has drawbacks such as high energy consumption. Artificial photosynthesis, which uses sunlight and semiconductor photocatalysts, could be promising as a more sustainable approach to producing H2O2. The development of efficient photocatalysts for this reaction is, thus, an interesting research target. Single-atom catalysts with sites such as Co-N4 units can be useful for the electrochemical reduction of O2 to H2O2. However, H2O2 photosynthesis has remained more challenging due to H2O2 decomposition at transition-metal sites under light irradiation.
Xiaojun Gu, Inner Mongolia University, Hohhot, China, Xiong Wen (David) Lou, City University of Hong Kong, China, and colleagues have developed a polymeric carbon nitride (CN) decorated with single-Zn sites that have tailorable local coordination environments. The team used zinc acetate to create asymmetric Zn-N3O, providing a CN/Zn-OAc catalyst that shows significantly improved photocatalytic H2O2 production activity under visible light irradiation compared with the common Zn-N4 moiety. The catalyst was prepared by mixing tubular polymeric CN with Zn(OAc)2·2H2O in ethanol at 80 °C, followed by annealing at 400 °C under an argon atmosphere.
According to the researchers, the asymmetric N/O coordination environment modulates the electronic structure of the Zn centers, facilitating O2 adsorption and the formation of the key intermediate *OOH. In addition, the Zn-N3O unit is inert to H2O2 decomposition under dark and light conditions. Overall, the work provides a simple approach to creating single-atom active sites with well-defined asymmetric configurations.
- Single Zn Atoms with Acetate‐Anion‐Enabled Asymmetric Coordination for Efficient H2O2 Photosynthesis,
Yunxiang Li, Yan Guo, Guilan Fan, Deyan Luan, Xiaojun Gu, Xiong-Wen (David) Lou,
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023.
https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202317572