Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) is an enzyme that is important in the development of B cells, a type of white blood cell. BTK is a potential drug target for the treatment of different human B-cell-related diseases. For example, BTK inhibition has been clinically validated as an anticancer treatment.
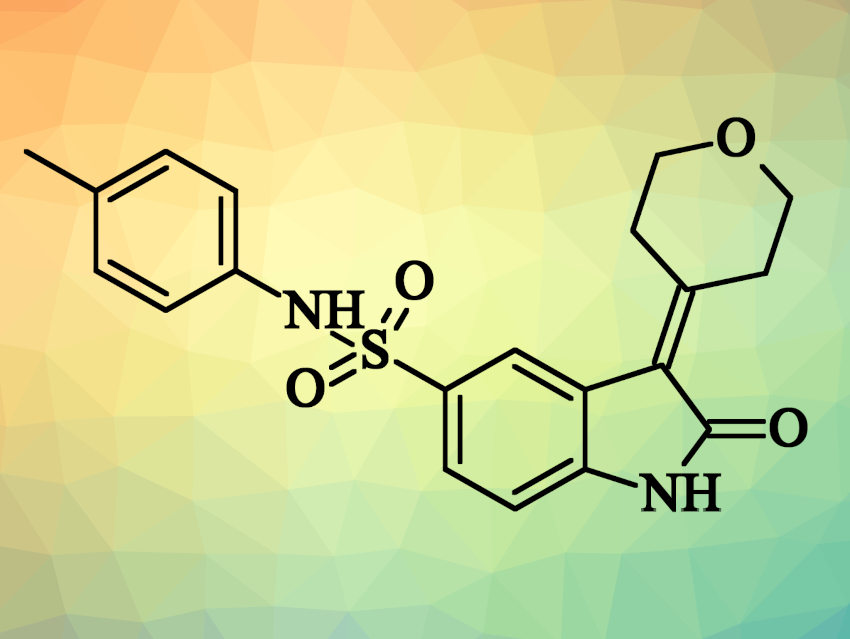
Searching for new, potent BTK inhibitors with minimal off-target effects, Viswanath Das, Palacký University and University Hospital Olomouc, Czech Republic, Rambabu Gundla, GITAM, Hyderabad, India, and colleagues have designed and synthesized oxindole sulfonamide derivatives (example pictured). The desired derivatives were synthesized via an efficient Knoevenagel condensation process involving the coupling of dihydro-2H-pyran-4(3H)-one with various sulfonamides. The biological activity of the compounds was assessed in a panel of BTK and non-BTK human cell lines comprising both cancerous and non-cancerous cells.
The team identified new derivatives that selectively inhibit the proliferation of BTK-high human B-cell lymphoma cells, with no-to-minimal cytotoxicity in non-BTK cancer and non-cancer cells. The most cytotoxic compound also showed promising activity in inhibiting BTK and downstream signaling cascades. Overall, the work could contribute to advancing the development of BTK inhibitors, with an emphasis on their effectiveness and safety in targeting cancers characterized by BTK expression.
- Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Oxindole Sulfonamide Derivatives as Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors,
Chandra Prakash Koraboina, Venkatanarayana Chowdary Maddipati, Narendran Annadurai, Soňa Gurská, Petr Dzubak, Marian Hajduch, Viswanath Das, Rambabu Gundla,
ChemMedChem 2023.
https://doi.org/10.1002/cmdc.202300511