C–H alkenylations are useful tools to form C–C bonds. Often, this type of reaction requires activated olefins. The use of unactivated alkenes in C–H olefination reactions can be challenging due to their lower reactivity. The dehydrogenative cross-coupling of alkenes with unactivated alkenes, for example, is not well-studied.
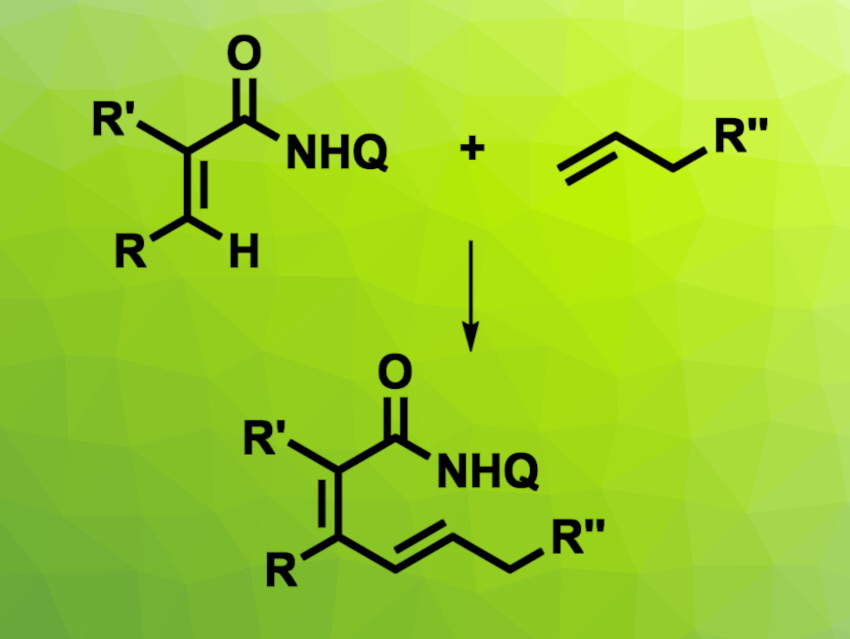
Masilamani Jeganmohan Indian Institute of Technology Madras, Chennai, India, and colleagues have developed a cobelt(III)-catalyzed oxidative cross-coupling of acrylamides with unactivated alkenes (pictured, Q = 8-quinolyl). The team reacted different substituted acrylamides with a range of functionalized olefins in the presence of Co(OAc)2·4H2O as a catalyst, Ag2CO3 as an oxidant, and NaOPiv·H2O as an additive, using 1,2-dichloroethene (1,2-DCE) as the solvent. The reactions were performed under air at 100 °C.
The desired coupling products were obtained in mostly good yields. The reaction tolerates α-alkene coupling partners with functional groups such as esters, amides, and ethers, as well as alkene-functionalized biologically relevant molecules. The team proposes a reaction mechanism that involves a vinylic C–H activation via deprotonation and a five-membered cobaltacycle intermediate.
- Dehydrogenative Cross-Coupling of α,β-Unsaturated Compounds with Unactivated Olefins via Co(III) Catalysis,
Ravichandran Logeswaran, Masilamani Jeganmohan,
Org. Lett. 2023.
https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.orglett.3c02095